 Standard deployment topology patterns overview
Standard deployment topology patterns overview
Authors: StevenBeard, TimFeeney, BreunReed, PaulEllis, ShubjitNaik Build basis: CE/CLM 6.x (with some restrictions)
This page complements the Standard Topologies Overview by providing diagrams and description of the main patterns that can be used for specific reasons within a CE/CLM deployment topology. They include only the parts of the deployment topology needed to present the pattern and not all of the other nodes that can be deployed within the wider topology.
For further Information on Jazz Security Architecture you can visit our jazz.net article Jazz Server Authentication Explained and our deployment wiki JAS Landing page For instructions to configure CE/CLM to authenticate via JAS as OIDC provider please visit Configure OIDC Authentication for CE/CLM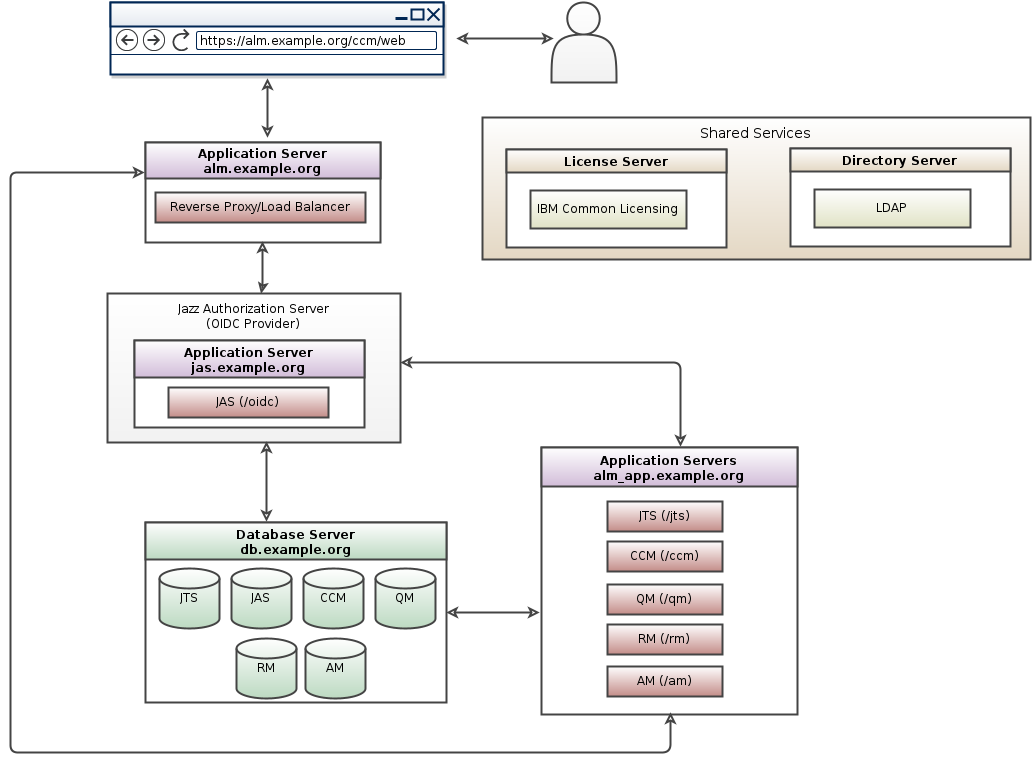
In this approach the user authentication is further delegated from JAS to another OIDC provider and this leads to redirections which some clients cannot do. Following are the limitations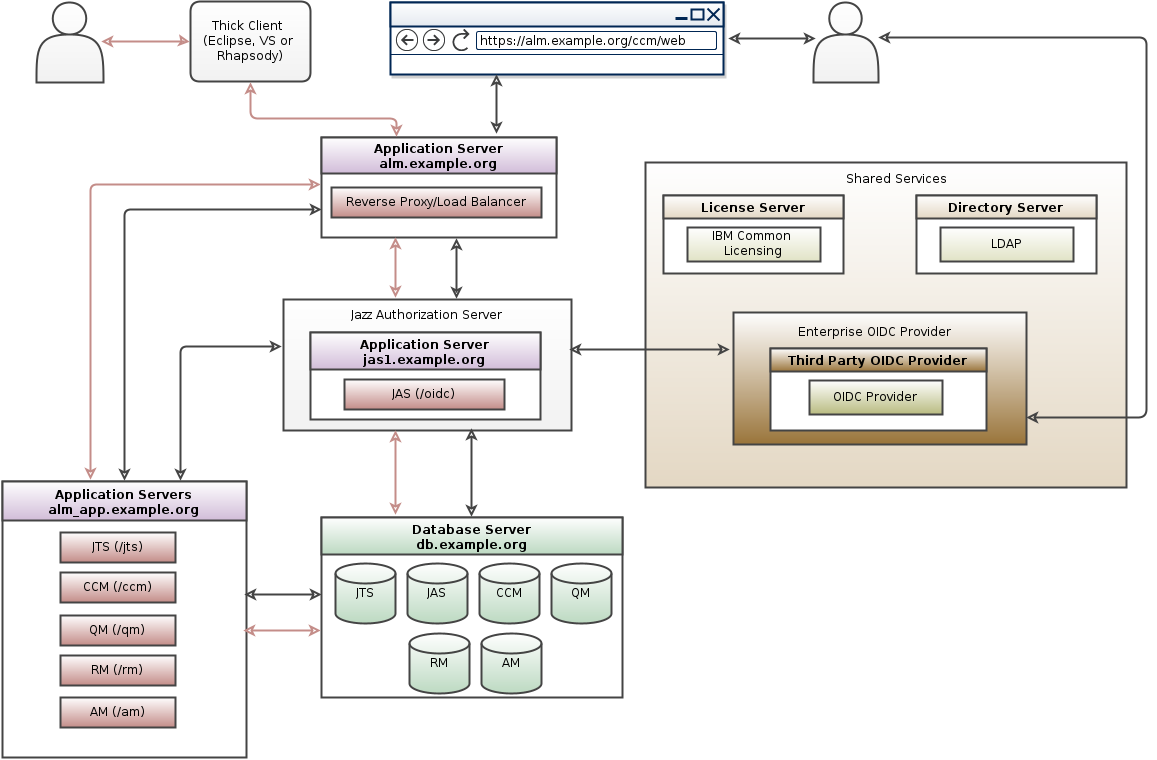
SAML is an OASIS open standard for representing and exchanging user identity, authentication, and attribute information. A SAML assertion is an XML formatted token that is used to transfer user identity and attribute information from the identity provider (IdP) of a user to a trusted service provider (SP) as part of completing an SSO request. For more information, see SAML web single sign-on. In this approach the user authentication is further delegated from JAS to a SAML Identity Provider, this leads to redirections which some clients cannot do. Following are the limitations
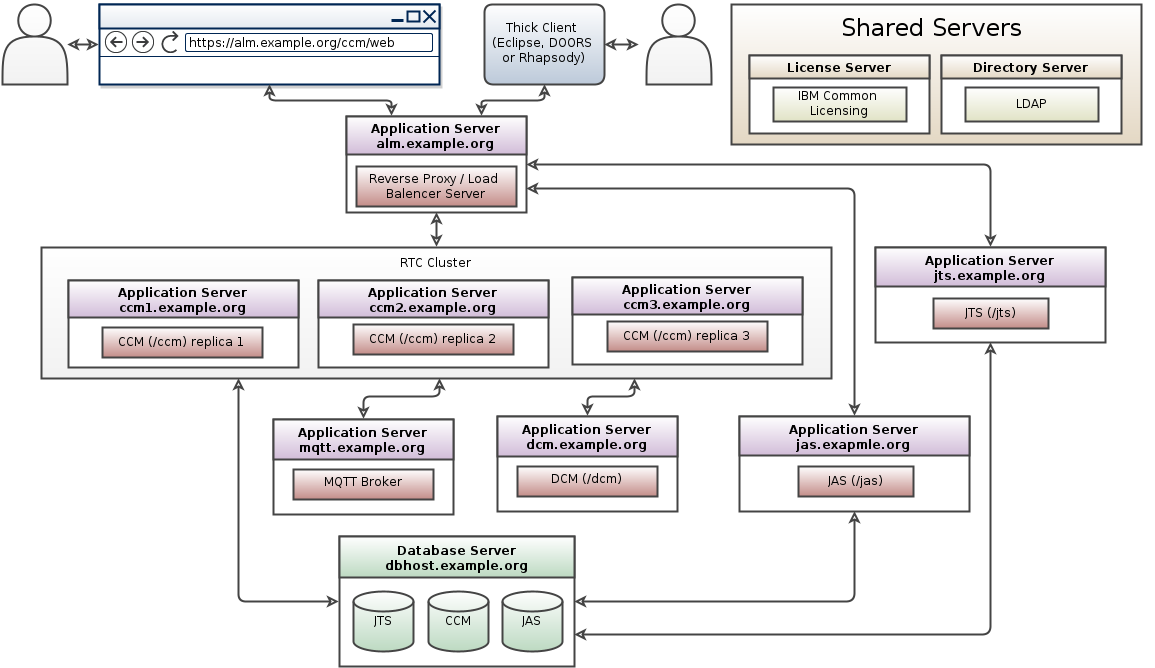
Rational Team Concert (RTC) clustering
- RTC clustering topology pattern for CE/CLM 6.0.5 and beyond:
IBM HTTP Server (IHS) and Jazz Authorization Server (JAS) Clustering
- IHS and JAS clustering topology pattern for CE/CLM 6.0.2 and beyond:
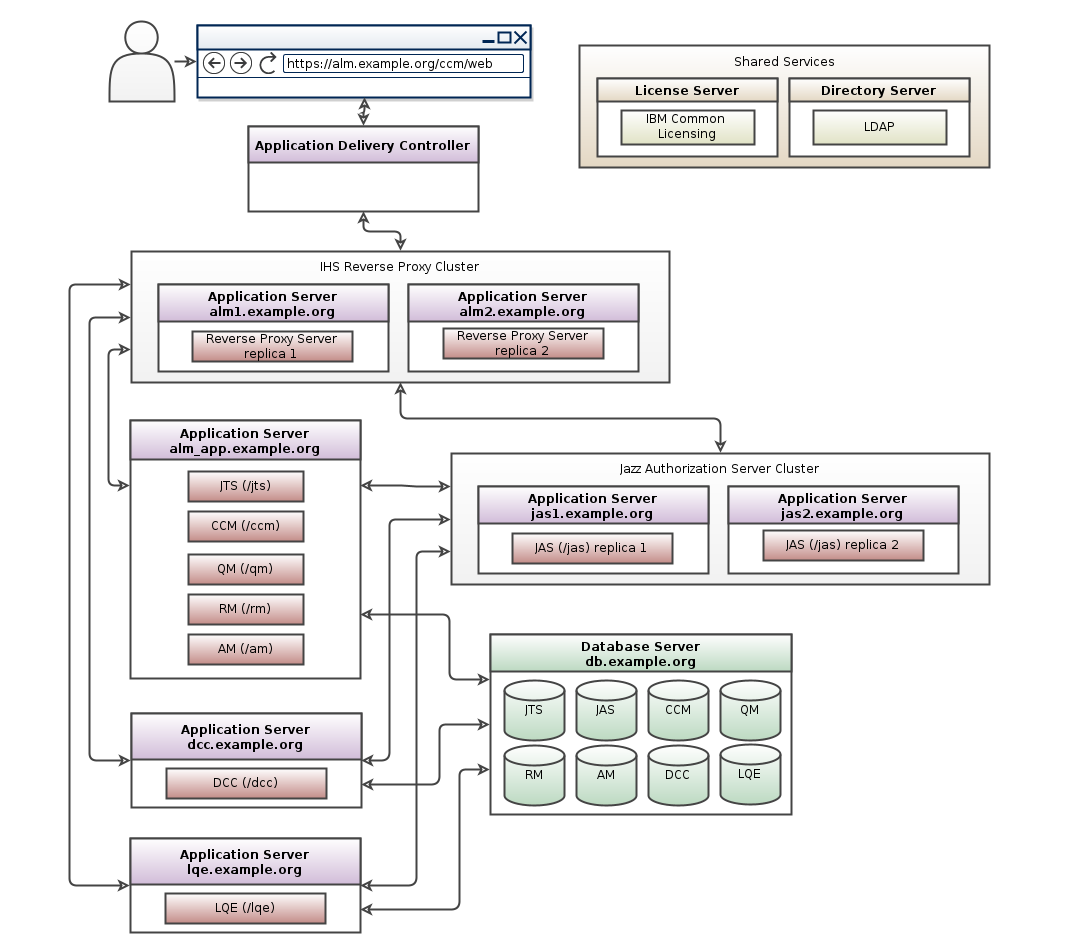
Modified Departmental patterns
- Modified Departmental topology pattern for CE/CLM 6.0.2 and beyond:
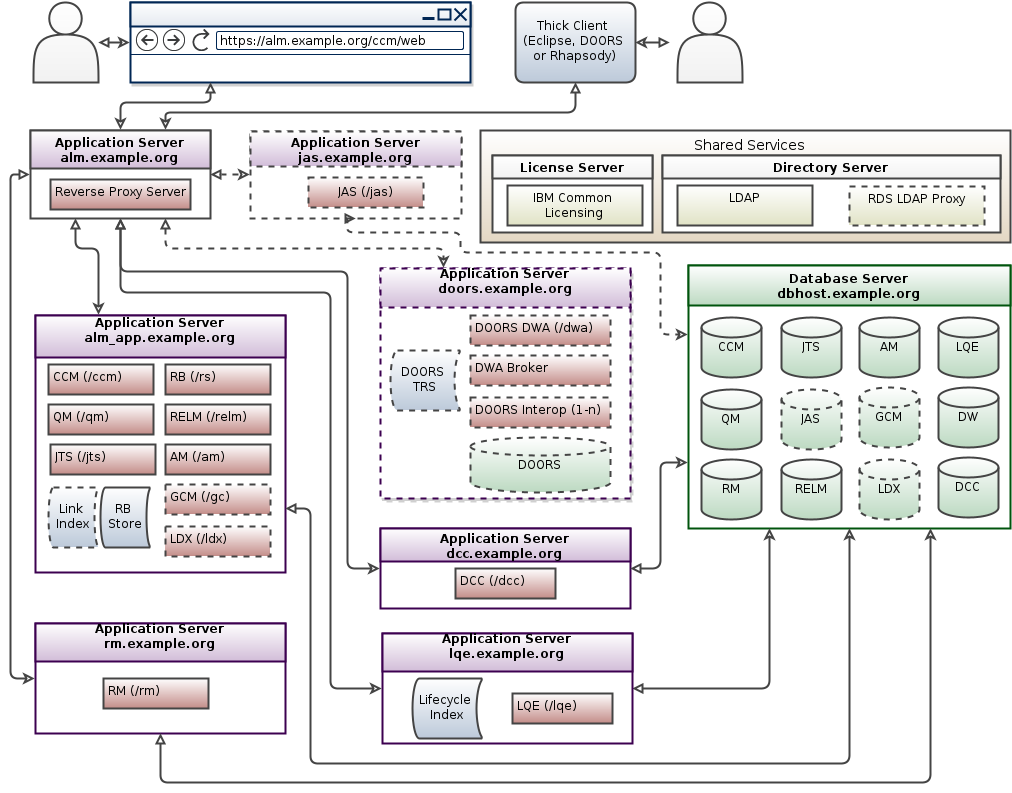
Multiple application servers of the same product
- Multiple application servers topology pattern for CE/CLM 6.x:
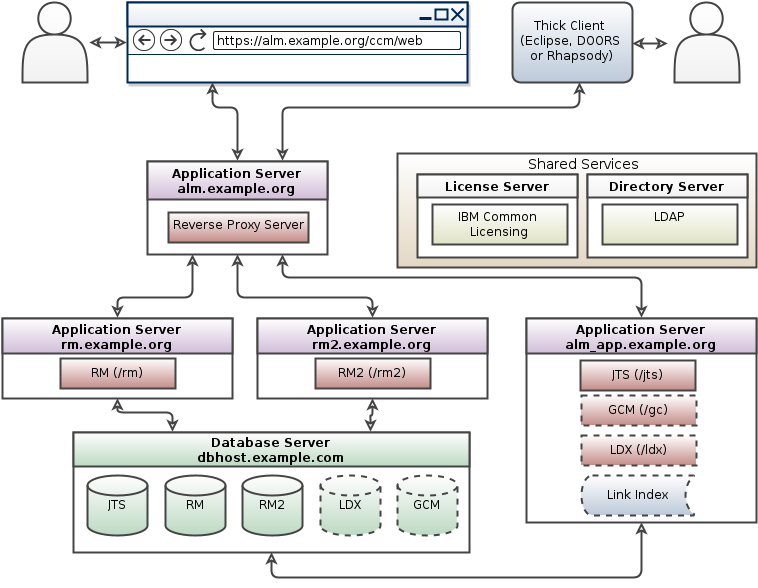
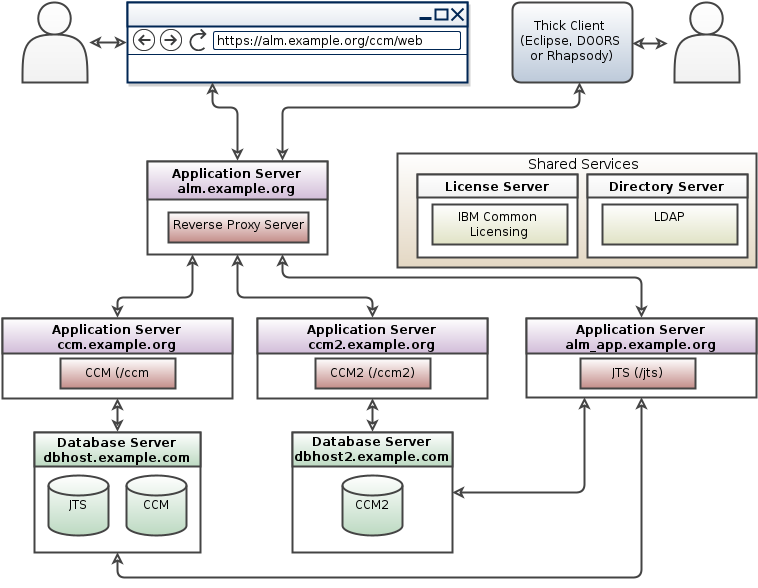
Multiple database servers
- Multiple database servers topology pattern for CE/CLM 6.x:
Security (OIDC, SCIM, SAML)
Jazz Authorization Server as the OpenID Connect Provider
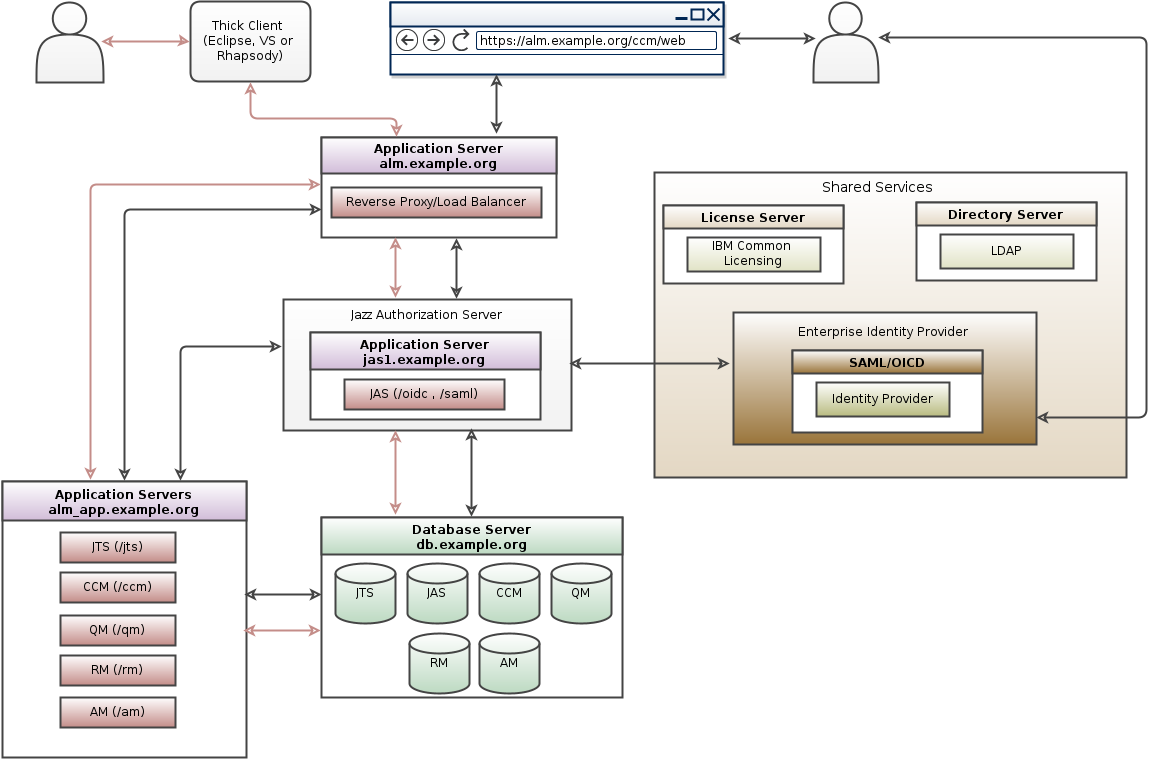
Starting with the Collaborative Lifecycle Management (CLM) Solution 6.0 software release, Jazz Security Architecture SSO is available as an authentication option. Based on OpenID Connect , authentication is NOT performed by the container hosting Jazz applications, but instead is delegated to a separate Jazz Authorization Server (JAS), which performs the role of an OpenID Connect provider (OP). Jazz Authorization Server is based on the IBM WebSphere Liberty profile.For further Information on Jazz Security Architecture you can visit our jazz.net article Jazz Server Authentication Explained and our deployment wiki JAS Landing page For instructions to configure CE/CLM to authenticate via JAS as OIDC provider please visit Configure OIDC Authentication for CE/CLM
- OIDC Topology pattern for CE/CLM 6.0 and beyond:

System for Cross-domain Identity Management (SCIM)
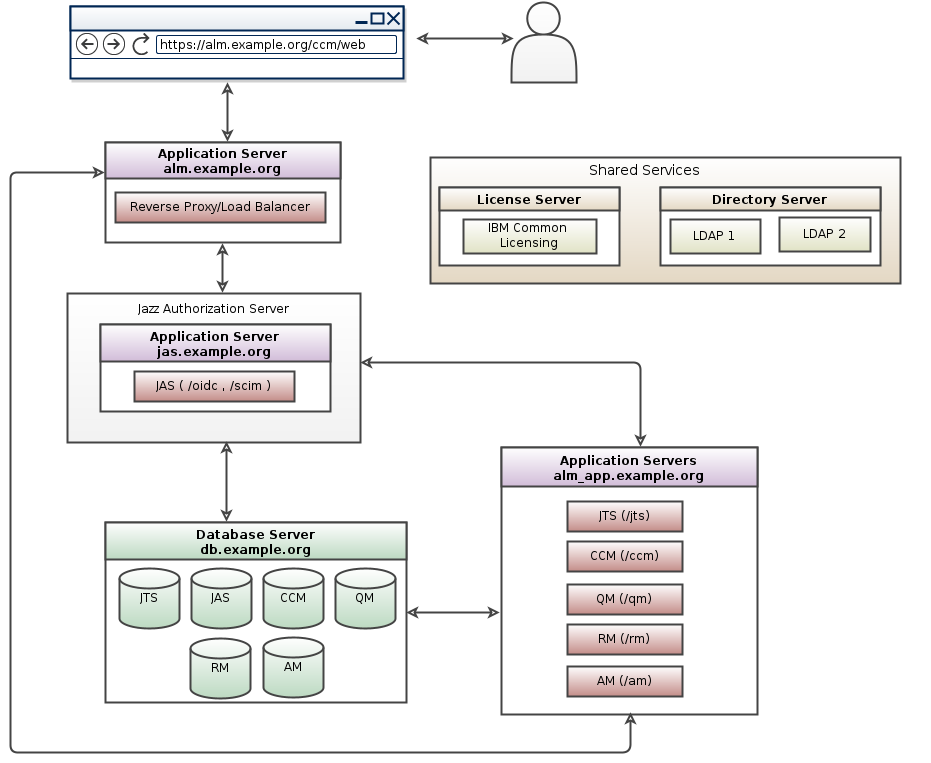
You can configure the Jazz Authorization Server (Liberty OpenID Connect Provider) to use the System for Cross-domain Identity Management (SCIM) for the WebSphere Application Server Liberty profile. SCIM is a standard for cloud-based identity management for single sign-on (SSO) in browsers. It is a RESTful protocol for identity account management operations. Starting with Collaborative Lifecycle Management (CLM) solution 6.0.5 software release, Jazz Authorization Server supports SCIM in the Liberty profile.Restriction : When you configure your Jazz Authorization Server to use the System for Cross-domain Identity Management (SCIM), you cannot use the Electronic signatures features in Rational Team Concert.
For instructions to configure JAS with SCIM please visit Configure JAS for SCIM
- SCIM Topology pattern for CE/CLM 6.0.5 and beyond:

Third Party OIDC Provider
You can configure Jazz Authorization Server (Liberty OpenID Connect Provider) to further delegate the user authentication to your standard, corporate OpenID Connect provider using the Liberty Social Login feature. Using this method we can delegate authentication from JAS to another OIDC provider.In this approach the user authentication is further delegated from JAS to another OIDC provider and this leads to redirections which some clients cannot do. Following are the limitations
- Authenticating through a Third Party OIDC provider works only for Browser based clients
- Thick Clients (Eclipse, Visual Studio) and Command line utilities can be configured to authenticate via JAS and hence JAS needs to be connected to the LDAP / Directory server that the Third Party OIDC provider works with.
- Third Party OIDC Provider Topology pattern for CE/CLM 6.0.6.1 and beyond:

SAML as Identity Provider
Starting in the Collaborative Lifecycle Management (CLM) version 6.0.1, Jazz Authorization Server supports Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) web browser single sign-on (SSO) which enables web applications to delegate user authentication to a SAML identity provider instead of a configured user registry.SAML is an OASIS open standard for representing and exchanging user identity, authentication, and attribute information. A SAML assertion is an XML formatted token that is used to transfer user identity and attribute information from the identity provider (IdP) of a user to a trusted service provider (SP) as part of completing an SSO request. For more information, see SAML web single sign-on. In this approach the user authentication is further delegated from JAS to a SAML Identity Provider, this leads to redirections which some clients cannot do. Following are the limitations
- Authenticating through a SAML Identity Provider for CLM works only for Browser based clients
- Thick Clients (Eclipse, Visual Studio) and Command line utilities can be configured to authenticate via JAS and hence JAS needs to be connected to the LDAP / Directory server that is configured with the SAML Identity Provider.
- SAML topology pattern for CE/CLM 6.0.1 and beyond:
Related topics:
Additional contributors:
Contributions are governed by our Terms of Use. Please read the following disclaimer.
Dashboards and work items are no longer publicly available, so some links may be invalid. We now provide similar information through other means. Learn more here.