Recommended SSE deployment topologies
Authors: ThomasPiccoli, StevenBeard, CarlosFerreiraBuild basis: The Rational solution for systems and software engineering (SSE), version 3.x, 4.x
Page contents
- Standard topologies overview
- Introduction and approach
- (SSE-E1) Enterprise Windows with Oracle and DOORS/DWA
- (SSE-E2) Enterprise Windows with Oracle and DNG
- (SSE-E4) Enterprise distributed Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) with DB2 and DNG
- (SSE-D3) Departmental Windows with Oracle
- (SSE-D4) Departmental Windows with Oracle and DNG
- Applying the topologies
- Datasheets and sizing guidelines
- Next steps
Standard topologies overview
This page describes the Recommended SSE Deployment Topologies for versions 3.x and 4.x. Refer to Standard deployment topologies overview for high-level description of the standard topologies, how they are categorized and their key characteristics. These recommended deployment topologies for the Rational solution for systems and software engineering (SSE) are a subset of the standard SSE deployment topologies. For the rest of the standard topologies, see Alternative SSE deployment topologies. Within this wiki, additional guidance and best practices will be developed about how to best instantiate these recommended topologies.Introduction and approach
These recommended topologies were chosen based upon the following criteria:- Those that are most commonly and successfully deployed to date by customers and internally within IBM
- Those that are based upon the most commonly available platforms, operating systems and middleware
- Those that are based upon technologies that customers, partners and the IBM Rational Field have the most experience with
- Those that are the focus of testing within IBM Rational.
(SSE-E1) Enterprise Windows with Oracle and DOORS/DWA
This enterprise topology uses Windows for the server operating systems. It includes DNG as the RM application. The applications are distributed across separate servers and WAS instances. A reverse proxy is used to ensure public URI stability. Oracle is used for the databases and is hosted on a separate server. Finally, licenses are served by a floating license server and Windows Active Directory Server provides the LDAP based user management.| Metadata Variable | Value |
| Operating System | Windows |
| Database Management System | Oracle |
| Application Server | WAS |
| License Management System | Floating |
| User Management System | Microsoft Active Directory |
| Other technologies | Reverse Proxy |
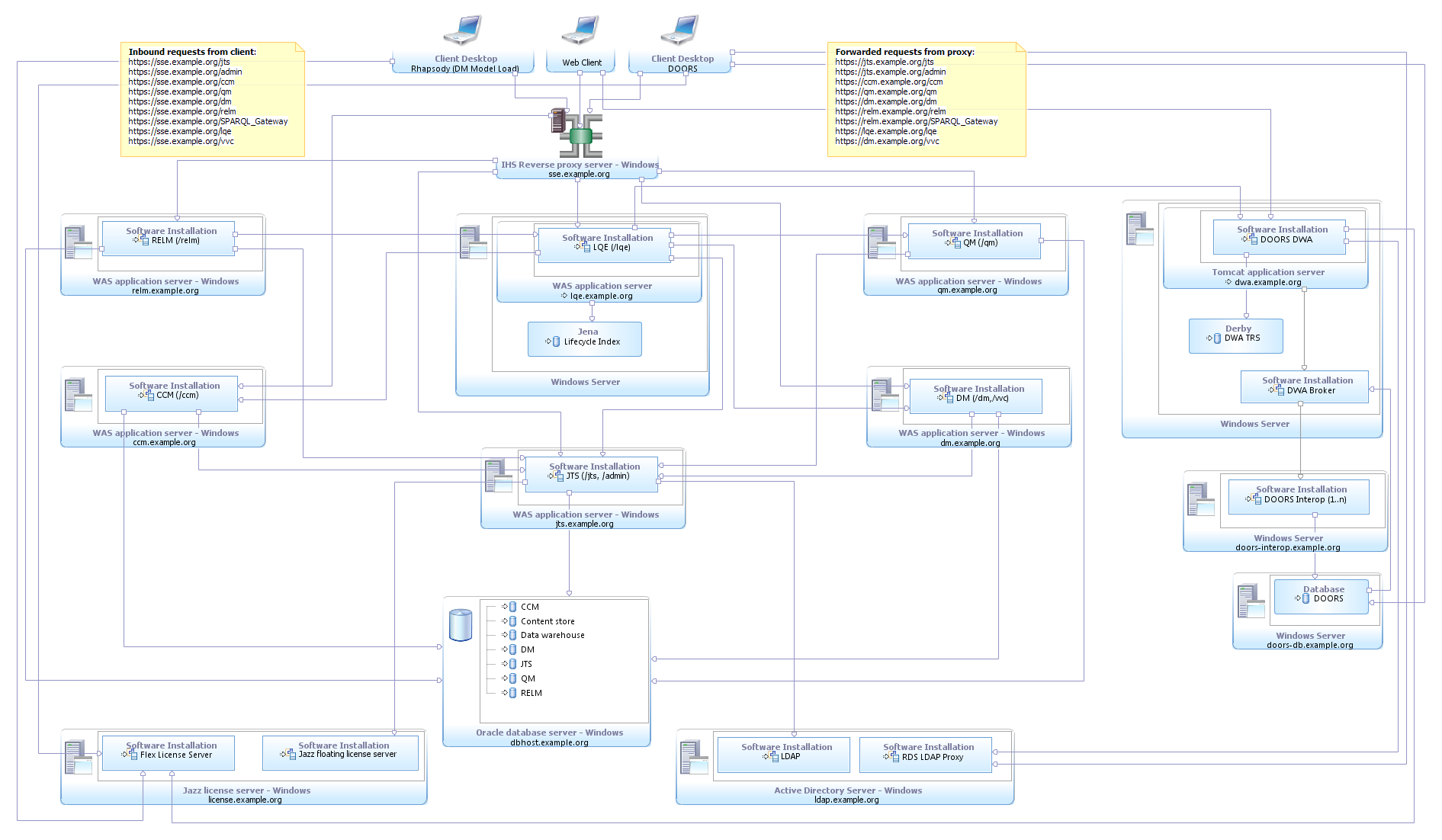
(SSE-E1) Enterprise Windows with Oracle and DOORS
| Server | Software |
| 1 | RDM, VVC, WAS |
| 2 | RELM, WAS |
| 3 | CCM, WAS |
| 4 | QM, WAS |
| 5 | JTS, WAS |
| 6 | Oracle |
| 7 | DWA, Broker, Tomcat |
| 8 | DOORS DB |
| 9 | LDAP Server |
| 10 | LQE, WAS |
| 11 | Reverse Proxy Server |
| 12 | License Server |
| 13 | DOORS Interops (1..n) |
(SSE-E2) Enterprise Windows with Oracle and DNG
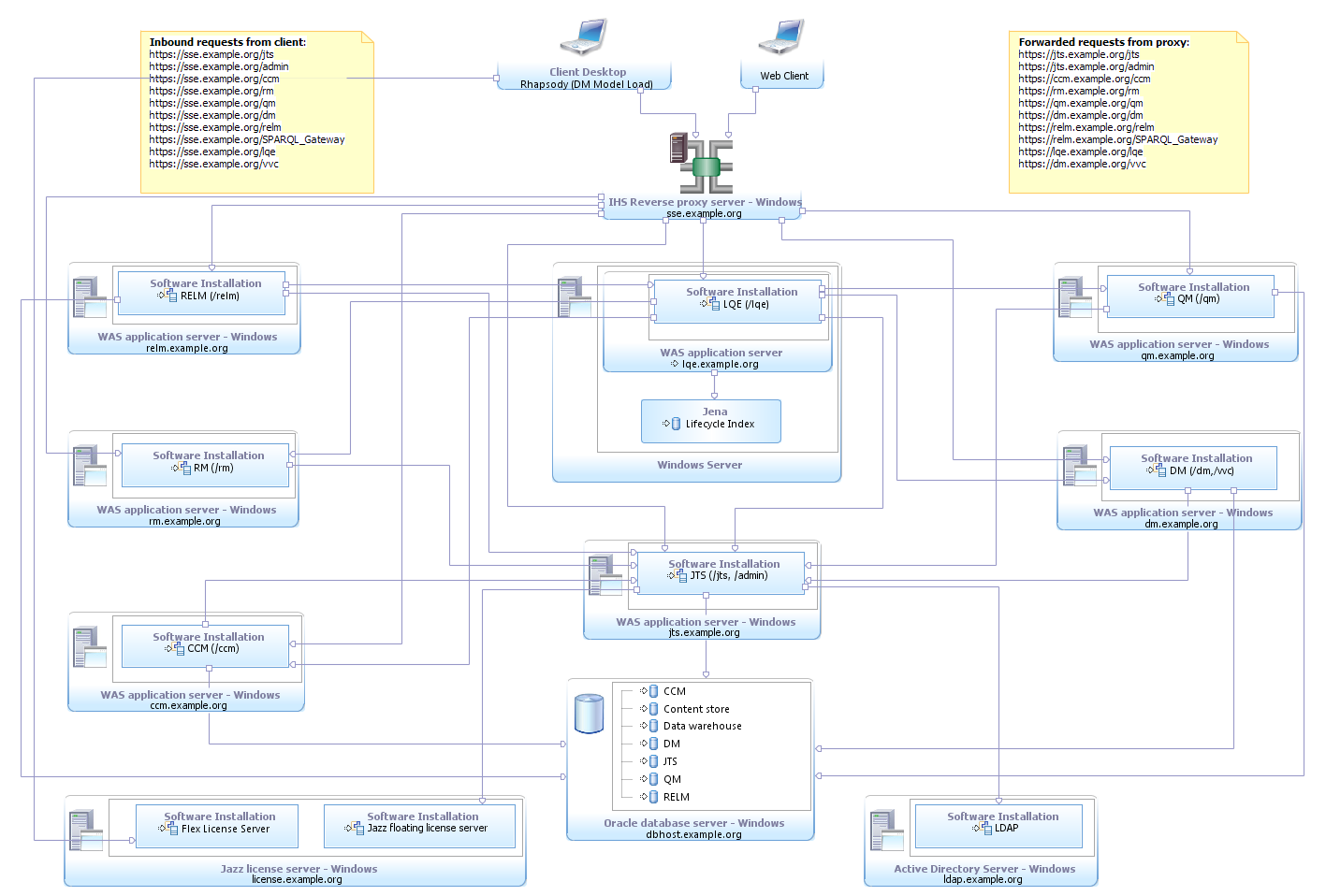
(SSE-E2) Enterprise Windows with Oracle and DNG
| Server | Software |
| 1 | RDM, VVC, WAS |
| 2 | RELM, WAS |
| 3 | CCM, WAS |
| 4 | RM, WAS |
| 5 | QM, WAS |
| 6 | JTS, WAS |
| 7 | Oracle |
| 8 | LDAP Server |
| 9 | LQE, WAS |
| 10 | Reverse Proxy Server |
| 11 | License Server |
(SSE-E4) Enterprise distributed Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) with DB2 and DNG
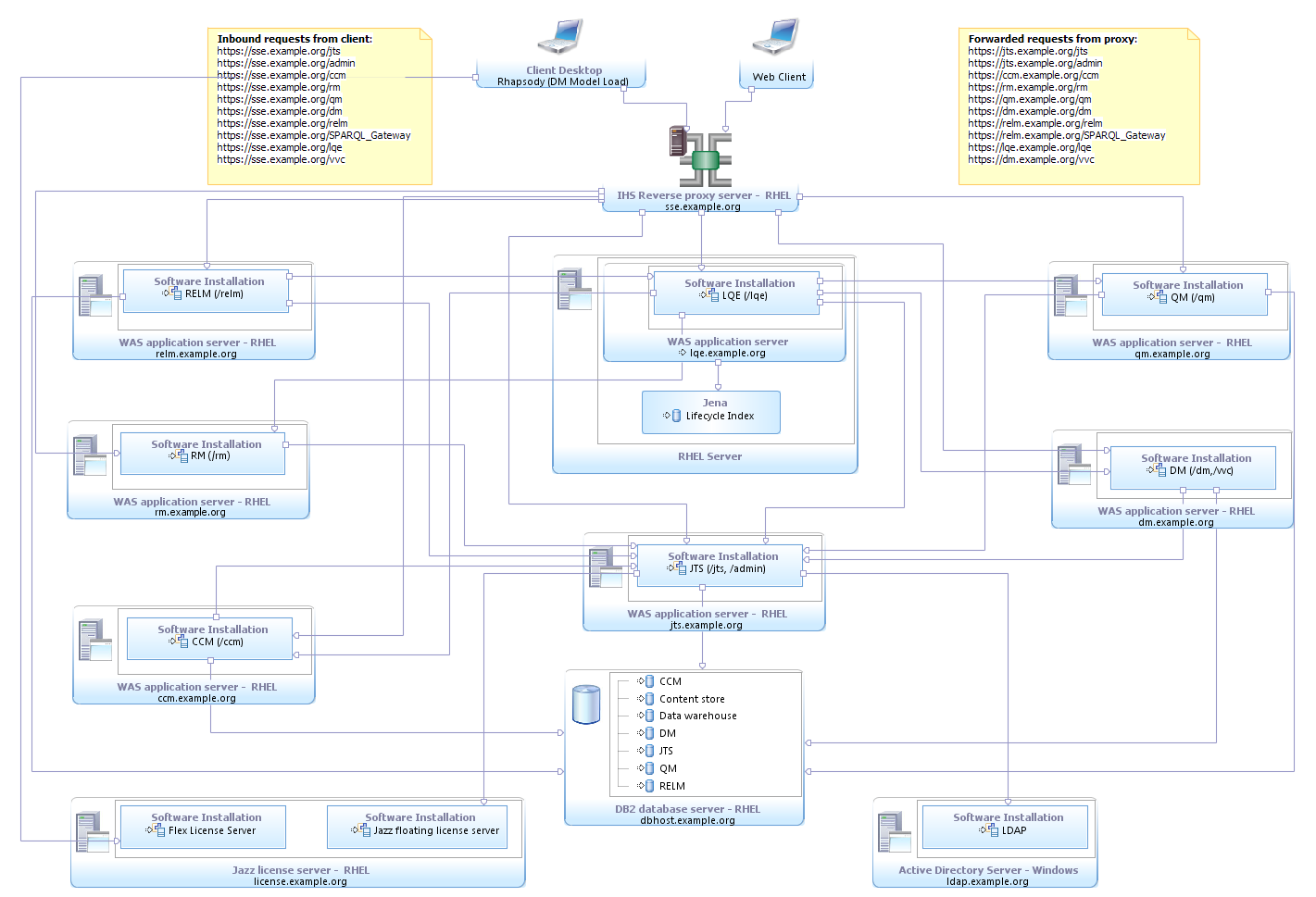
(SSE-E4) Enterprise distributed Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) with DB2 and DNG
| Server | Software |
| 1 | RDM, VVC, WAS |
| 2 | RELM, WAS |
| 3 | CCM, WAS |
| 4 | RM, WAS |
| 5 | QM, WAS |
| 6 | JTS, WAS |
| 7 | DB2 |
| 8 | LDAP Server |
| 9 | LQE, WAS |
| 10 | Reverse Proxy Server |
| 11 | License Server |
(SSE-D3) Departmental Windows with Oracle
Departmental or small organisation topology, using DNG as RM tool. Uses 3 Windows servers, with Oracle database on its own server, LQE on another server, and all other applications on third server. Uses Microsoft Active Directory as identity management.| Metadata Variable | Value |
| Operating System | Windows |
| Database Management System | Oracle |
| Application Server | WAS |
| License Management System | Floating |
| User Management System | Microsoft Active Directory |
| Other technologies | Reverse Proxy |
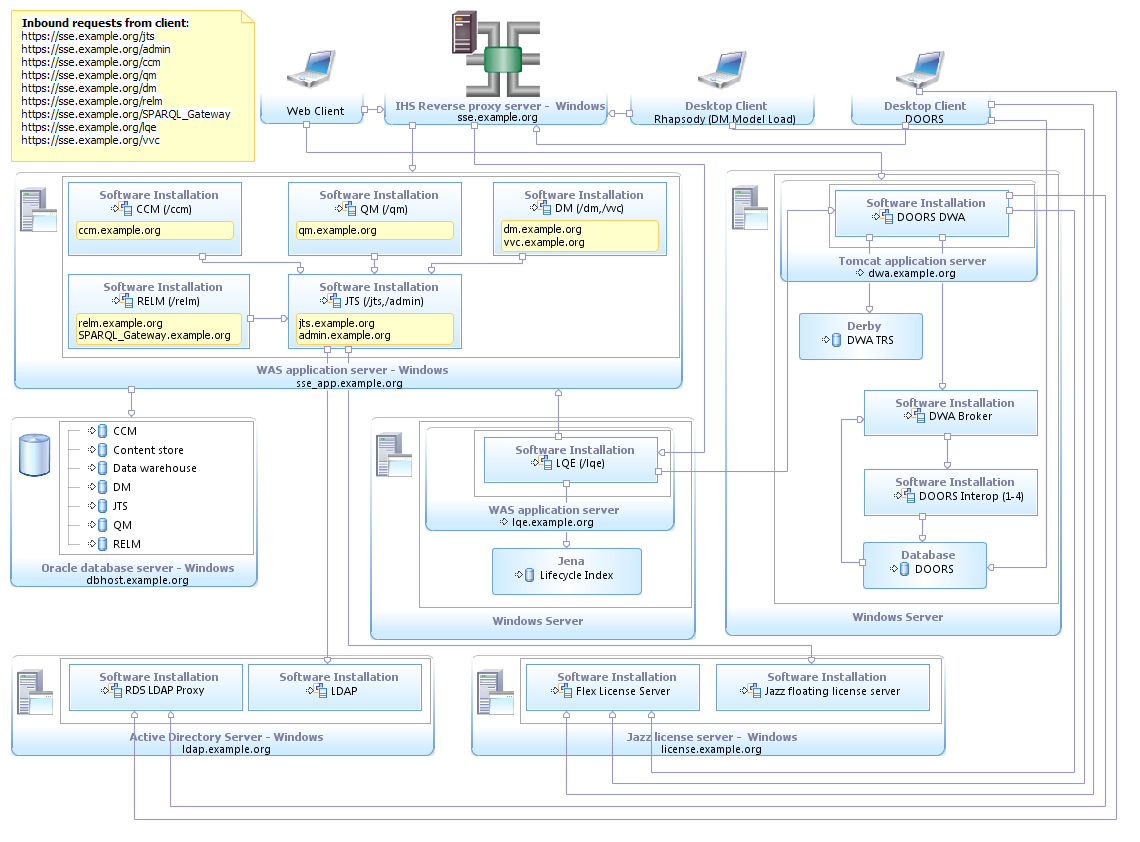
(SSE-D3) Departmental Windows with Oracle and DOORS
(SSE-D4) Departmental Windows with Oracle and DNG
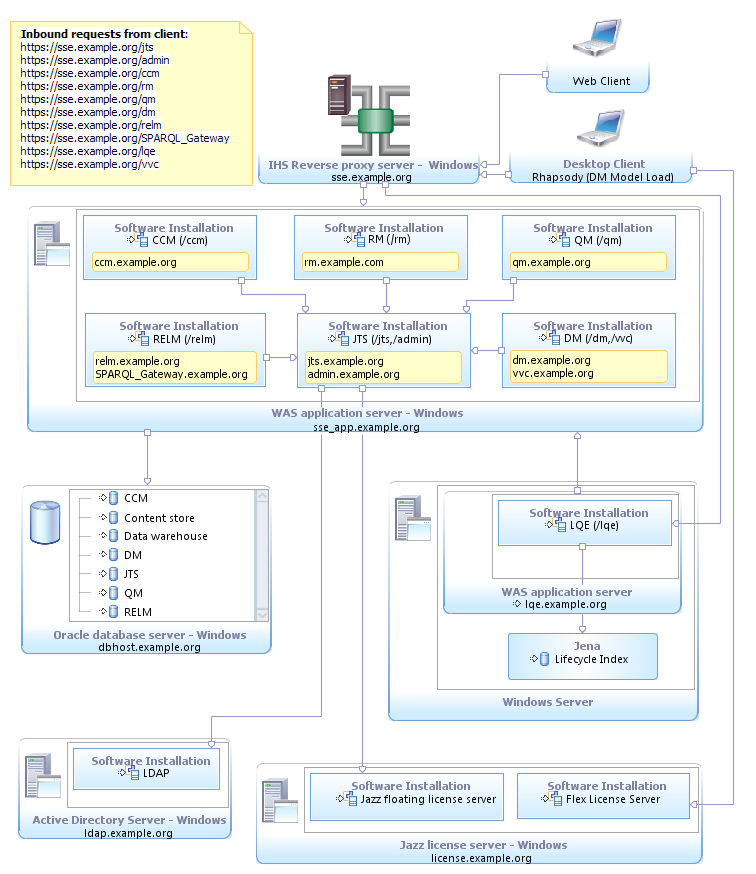
(SSE-D4) Departmental Windows with Oracle and DNG
Applying the topologies
Every customer's environment is different with unique, necessary and often immutable requirements and constraints. We recognize that these standard topologies may not provide enough detail to make them immediately implementable in some customer environments, but we wanted to describe several topologies with enough variability to give an indication of what is possible and where our recommendations start. While we recommend customers start with a standard topology that is most applicable to them, we recognize they will need to make changes and customizations to support their own unique requirements and constraints. IBM will support your own implementations, but may ask you to describe which topology is most applicable to your deployment and ask you to document what is unique in your environment to expedite any potential support situation. To aid you in documenting your chosen deployment topology, we have made the following Rational Software Architect (RSA) model files available:- CLM standard topologies
- CLM standard topologies 5.0.2
- SSE standard topologies 4.0.3 and 4.0.4
- SSE standard topologies 4.0.5
- SSE standard topologies 4.0.6
- SSE standard topologies 5.0.0
- SSE standard topologies 5.0.1
- SSE standard topologies 5.0.2
Datasheets and sizing guidelines
Find CLM-specific performance datasheets, sizing guidelines and performance-related case studies on the Performance datasheets and sizing guidelines page.Next steps
This topic is meant to briefly introduce these standard topologies and describe how they might be applied. Work is already underway to build upon and apply them. Subsequent updates to this topic and supporting topics will provide additional insight into their usage. Future updates to this topic or supporting topics may cover:- Deeper look at select topologies
- Provide suggested tuning parameters
- Consider high availability database topologies
- Begin to expand this topology model into other domains
- Discussion of strategic integrations with other Rational and non-Rational products.
Related topics: Deployment planning and design, Alternative SSE deployment topologies
External links:
- None
Additional contributors: None
Deployment.RecommendedSSEDeploymentTopologies moved from Deployment.StronglyRecommendedSSEDeploymentTopologies on 2013-05-15 - 14:29 by Main.sbeard -
Contributions are governed by our Terms of Use. Please read the following disclaimer.
Dashboards and work items are no longer publicly available, so some links may be invalid. We now provide similar information through other means. Learn more here.