This article demonstrates using OAuth 1.0a to access protected resources of ELM using REST Client browser extension to Firefox. It introduces the URLs to use for each Leg of the authentication process and unique aspects for each application.
You will need Admin User Access to the Application for this. Once you login as an Admin user to the application, you can register a consumer from the Admin/Consumers page. You can reach this page using the url of the form:
Alternatively, one can make use of the additional provisions that were made to Root Services document of ELM applications to provides URLs to register consumers and approve them. For more details, refer to the addendum here: https://jazz.net/wiki/bin/view/Main/RootServicesSpecAddendum2
Once registered, make a note of the consumer key and the secret. We will need them in the Auth flow.
2. Note the URLs to use for authentication flow.
These URLs are accessed from the Rootservices document for the application that owns the protected resources that you wish to access. i.e., if you wish to access RM resources, you will need to access RM root services document. To access the rootservices document, you can use url of the form:
With the Consumer Key and Secret and the URLs, we are ready to begin the 3 legged Authorization flow. This flow starts with getting a Request Token qouting the Consumer Key/Secret. Authorizing the Token using an User's login and finally exchanging the Authorized Request Token for an Access Token. The Access Token can then be used to access Protected resources from the application.
Now, lets look at the auth flow in detail
* Additional OAuth-related Properties in Root Services Documents
* Jazz Foundation Core Security
Steps
Getting Started
1. Register a ConsumerYou will need Admin User Access to the Application for this. Once you login as an Admin user to the application, you can register a consumer from the Admin/Consumers page. You can reach this page using the url of the form:
https://<host>:<port>/<appcontextroot>/admin#action=com.ibm.team.repository.admin.configureOAuth Alternatively, one can make use of the additional provisions that were made to Root Services document of ELM applications to provides URLs to register consumers and approve them. For more details, refer to the addendum here: https://jazz.net/wiki/bin/view/Main/RootServicesSpecAddendum2
Once registered, make a note of the consumer key and the secret. We will need them in the Auth flow.
2. Note the URLs to use for authentication flow.
These URLs are accessed from the Rootservices document for the application that owns the protected resources that you wish to access. i.e., if you wish to access RM resources, you will need to access RM root services document. To access the rootservices document, you can use url of the form:
https://<host>:<port>/<appcontextroot>/rootservices <jfs:oauthRequestTokenUrl rdf:resource="https://<host>:<port>/jts/oauth-request-token"/> <jfs:oauthUserAuthorizationUrl rdf:resource="https://<host>:<port>/jts/oauth-authorize"/> <jfs:oauthAccessTokenUrl rdf:resource="https://<host>:<port>/jts/oauth-access-token"/> With the Consumer Key and Secret and the URLs, we are ready to begin the 3 legged Authorization flow. This flow starts with getting a Request Token qouting the Consumer Key/Secret. Authorizing the Token using an User's login and finally exchanging the Authorized Request Token for an Access Token. The Access Token can then be used to access Protected resources from the application.
Now, lets look at the auth flow in detail
Perform Oauth 3 legged flow
The section for Application to Application authentication in the article https://jazz.net/wiki/bin/view/Main/JFSCoreSecurity shows the typical flow. In this article we shall perform that flow using REST Client.- 1st Leg: Get Request Token
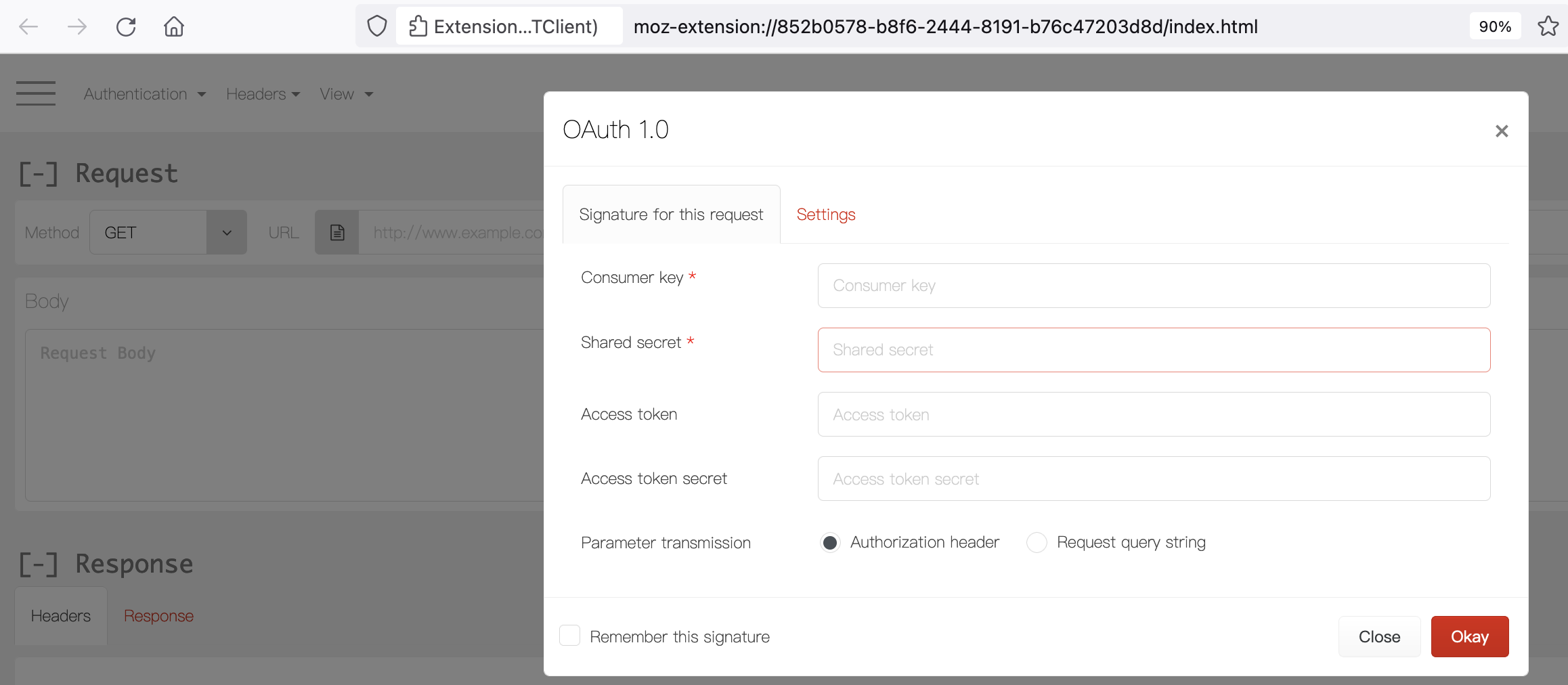
- 2nd Leg: Authorise Request Token This requires a manual intervention, with a specific userís credentials using application login prompt
- 3rd Leg: Get Authorised Access Token
Accessing protected resource using the Authorised Access Token
Application Specifics
ERM Specifics
ERM Delegates the authentication to JTS. Hence unlike in the apps which manage their authentication, for RM the URL's for request token, authorize and access token are JTS based.EWM Specifics
ETM Specifics
Conclusion
work item links for more details
wiki links
Related topics:
* TN0013: Jazz Server Authentication Explained* Additional OAuth-related Properties in Root Services Documents
* Jazz Foundation Core Security
External links:
Additional contributors: TWikiUser, TWikiUser
Contributions are governed by our Terms of Use. Please read the following disclaimer.
Dashboards and work items are no longer publicly available, so some links may be invalid. We now provide similar information through other means. Learn more here.
