Query and Search indices management in the Rational solution for Collaborative Lifecycle Management
Part 2: Indices storage and management: Backup, recovery and recreation
Authors: RichWatts, TimFeeney Build basis: Rational solution for Collaborative Lifecycle Management v4.0.x and 5.0.x, v6.0.x, v7.0.x
The purpose of this series of articles is to provide a basic understanding of the indexing processes in Jazz used by information query and search features, the technologies involved and to provide guidance on the associated administering tasks. We will also briefly review some details on the base architectural details, and how information is stored and queried in the different CLM applications.
This second part of the article series will discuss different administering tasks related with indices management and indices storage details.
For the remainder of this article is important to keep in mind what querying and indexing technology is applicable for each CLM application. You can find detailed information in the Part 1 of this article, summarized in the section called "Recap: Search and indexing in your CLM deployment".
In this article we will cover the storage recommendations and administration tasks for maintaining the indices used by JFS and FullText services. The Item Query Service is not relevant for this discussion as the query and indices features are supported by the database.
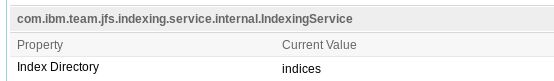
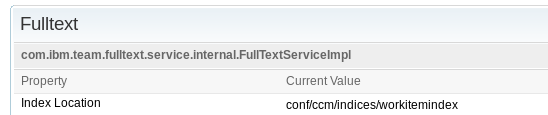 Keep in mind that all CLM applications but RM have a "teamserver.properties" file for the application configuration parameters such as database location, and the storage of JFS and FullText indices. In 5.0.x, RM no longer uses JTS for storage, querying and indexing and does have a teamserver.properties file. Note also that although all these properties exist in all the "teamserver.properties" files, the actual relevance of them in a particular CLM application will depend on the query and search technologies being used. Refer to Part 1 of this article for this mapping information between CLM applications and indexing technologies in use.
Now we have reviewed which configuration properties are used to configure the indices storage: how are those configuration properties used to determine the storage on disk?
Keep in mind that all CLM applications but RM have a "teamserver.properties" file for the application configuration parameters such as database location, and the storage of JFS and FullText indices. In 5.0.x, RM no longer uses JTS for storage, querying and indexing and does have a teamserver.properties file. Note also that although all these properties exist in all the "teamserver.properties" files, the actual relevance of them in a particular CLM application will depend on the query and search technologies being used. Refer to Part 1 of this article for this mapping information between CLM applications and indexing technologies in use.
Now we have reviewed which configuration properties are used to configure the indices storage: how are those configuration properties used to determine the storage on disk?
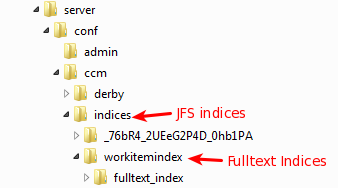 This storage location can be modified by changing the value of the reviewed properties: using the Advanced Properties wizard (recommended), or by modifying the application's "teamserver.properties" file. Changing any of these values need the application to be restarted to take effect. Such a storage location change will create the empty folders to store the new indices contents, but no old indices will be migrated automatically: you will need to copy over from the old location the indices with the application shut down or perform a reindex to regenerate them in the new location.
This storage location can be modified by changing the value of the reviewed properties: using the Advanced Properties wizard (recommended), or by modifying the application's "teamserver.properties" file. Changing any of these values need the application to be restarted to take effect. Such a storage location change will create the empty folders to store the new indices contents, but no old indices will be migrated automatically: you will need to copy over from the old location the indices with the application shut down or perform a reindex to regenerate them in the new location.
Indices Storage
Indices storage location
The storage of the indices is determined by a couple of application configuration properties, one for each type of index (JFS or FullText). These properties appear in the teamserver.properties file with the following default values after initial application post-installation setup:com.ibm.team.jfs.index.root.directory=indices com.ibm.team.fulltext.indexLocation=conf/<APP>/indices/workitemindexFor example in a typical CCM application deployment, "<APP>" would be "ccm". These teamserver.properties file entries have the corresponding parameter options in the Advanced Properties wizard for each application, which is accessed through the url of the form: https://<server>:<port>/<contextRoot>/admin#action=com.ibm.team.repository.admin.configureAdvanced
- JFS index

- FullText index
 Keep in mind that all CLM applications but RM have a "teamserver.properties" file for the application configuration parameters such as database location, and the storage of JFS and FullText indices. In 5.0.x, RM no longer uses JTS for storage, querying and indexing and does have a teamserver.properties file. Note also that although all these properties exist in all the "teamserver.properties" files, the actual relevance of them in a particular CLM application will depend on the query and search technologies being used. Refer to Part 1 of this article for this mapping information between CLM applications and indexing technologies in use.
Now we have reviewed which configuration properties are used to configure the indices storage: how are those configuration properties used to determine the storage on disk?
Keep in mind that all CLM applications but RM have a "teamserver.properties" file for the application configuration parameters such as database location, and the storage of JFS and FullText indices. In 5.0.x, RM no longer uses JTS for storage, querying and indexing and does have a teamserver.properties file. Note also that although all these properties exist in all the "teamserver.properties" files, the actual relevance of them in a particular CLM application will depend on the query and search technologies being used. Refer to Part 1 of this article for this mapping information between CLM applications and indexing technologies in use.
Now we have reviewed which configuration properties are used to configure the indices storage: how are those configuration properties used to determine the storage on disk?
- If using an absolute path value to specify the location of the indices storage, this path location will be used.
- If using relative path (as the default configuration shown earlier), the behavior will be:
- JFS index ("com.ibm.team.jfs.index.root.directory" property): the actual path will be based on the application configuration directory. For example, C:\IBM\JazzTeamServer\server\conf\CCM
- FullText ("com.ibm.team.fulltext.indexLocation" property): in this case, the contents location path will be based on the application relative runtime location. If your CLM application is running on Tomcat this will be the same as the application configuration directory; if your CLM application is running on WebSphere Application Server, this will be the profile path, for example: /<WAS_ROOT>/profiles/AppSrv01/
 This storage location can be modified by changing the value of the reviewed properties: using the Advanced Properties wizard (recommended), or by modifying the application's "teamserver.properties" file. Changing any of these values need the application to be restarted to take effect. Such a storage location change will create the empty folders to store the new indices contents, but no old indices will be migrated automatically: you will need to copy over from the old location the indices with the application shut down or perform a reindex to regenerate them in the new location.
This storage location can be modified by changing the value of the reviewed properties: using the Advanced Properties wizard (recommended), or by modifying the application's "teamserver.properties" file. Changing any of these values need the application to be restarted to take effect. Such a storage location change will create the empty folders to store the new indices contents, but no old indices will be migrated automatically: you will need to copy over from the old location the indices with the application shut down or perform a reindex to regenerate them in the new location.
Indices storage recommendations
We recommend the following configurations for indices storage management:- Storage location definition: when deploying your CLM solution, it is strongly recommended to modify the indices configuration specifying a full path location. Moreover, placing the indices in a location different from the default one it's preferred so they don't get accidentally deleted, for example, when uninstalling after an upgrade. For your enterprise deployment it is recommended to plan your installation storage layout with the indices storage in mind.
- Local vs. network location: general recommendation is to keep indices local to the servers so performance is optimal
- Network storage location: if using a network storage, the ideal characteristics of such storage are:
- Try to avoid connection over ethernet: in case of connectivity disruptions it may end up resulting in indices corruption
- Low latency connection link connection advised (e.g, SAS, Fibre Channel or InfiniBand)
- If possible try to use a file system that has capabilities for HA and redundancy(e.g, SAN or RAID 10)
Indices in a CLM High Availability deployment
Enterprise level deployments usually consider one of the possible HA configurations for the CLM solution. We will review some considerations for the inexing storage in these configurations:- Using a local storage for each node is the preferred configuration. In this case, should a failover be needed, you will have to copy the indices from the active to the backup server as part of this failover operation, to make them available updated and in sync with the repository. If no copy is possible then a reindex or a recovery from backup (of indices and repository), will be needed. This approach will require more time and operations in case of a failover, but it's simpler to set up and usually will perform better. Jazz indices are now able to recover well if information in the database is ahead of the corresponding index so copying from local storage to the backup server is no longer needed making setup for this scenario quite efficient.
- A shared storage to hold the indices for the active and backup servers can also be used. This will make the indices available in an updated state for the backup server in case of a failover operation with no further operation; e.g. the backup server will get the current state of information of the indices.
Indices Administration Tasks
This section of the article will high-light some of the typical administration tasks that you may need to perform for the indices maintenance.Backup and Recovery
Given the importance that the indices have for querying and searching for information, it is crucial that you consider the indices backup and recovery procedures as part of your general CLM backup strategy. The backup of the indices should be taken along with the database to ensure information consistency: to have an snapshot of database information and indices content. For this backup process however, we need to differentiate how the indices in play differ in nature:- JFS indices: repository tools commands are available to perform a backup of these files automatically. An example of such command for performing the backup of JFS indices for the Jazz Team Server application would be as follows:
repotools-jts -backupJFSIndexes repositoryURL=https://JTS_SERVER:JTS_SERVER_PORT/jts adminUserID=****** adminPassword=****** toFile=FILELOCATION_AND_NAME
- Fulltext index: there is no way of ensuring a consistent backup of the files of this indexing technology without performing a server shutdown. Therefore, to make sure that the indices are consistent with database information, the application should be first stopped/shut down to perform the backup copy. Note that this type of indices are updated synchronously on information update, so failing to stop the application for performing the backup could result in a corrupted copy or an invalid backup because of lost information events. Note CLM 4.0.5 versions and later: from that version the JFS indices online backup command also performs a backup of the FullText indices. However, the nature of such indices remains still the same as previously described (built synchronously).
Recreation of indices
The indices can be recreated. The situations in which you will have to consider indices recreation are:- In case of system recovery if no proper backup exists
- In case of indices storage failure
- In situations where where you are instructed to recreate them by Support, or by the official product documentation of another administrator task.
- JFS indices recreation: repotools-
.bat -reindex all. Note the importance of the "all" parameter, without it just a subset of the indices would be recreated. Check complete command syntax details here. An example of recreating JFS indices for JTS application:
repotools-jts.bat -reindex all
- Fulltext indices recreation: repotools-
.bat -rebuildTextIndices. Remember that this recreation is only useful for CCM and QM applications, which are the ones where this indexing technology is used. *NOTE: Starting in v7.0, RM does use this indexing technology, and thus rebuildTextIndices is applicable to RM. Check complete command syntax details here. An example of recreating Fulltext indices for CCM application:
repotools-ccm.bat -rebuildTextIndices
Both commands need the server to be shut down before executing them. The time for recreating the indices can take long depending on how big your repository is.
The example commands shown are for Windows platform based deployments. Corresponding commands for Unix/Linux platform deployments exist. Check the official documentation in the provided Information Center.
Compacting indices
JFS RDF indices can grow large in time. A command is available that will allow you to compact them and save some space:
repotools-ccm.bat -compactDB
The compete syntax of the command would be:
repotools-jts.sh -compacttdb srcdir=<RDF indices location> tempdir=<temporary location to use>
There are two important considerations for this command to be run:
- The recommended size for the temporary location to use is double size of the current one for the indices to compact
- Not an issue in 5.0.2 or later You have to specify the exact location of the indices folder to compact, for example:
conf/jts/indices/<numericID>/jfs-rdfindex. There is an enhancement request open to simplify this: repotools compacttdb should iterate through the indices folder to find the index to compress.
Verifying indices
As of 5.0.1, a repotools command exists to verify JFS indices to ensure they are not corrupt. The syntax is as followsrepotools-<application> -verifyindexes [teamserver.properties=conf/<application>/teamserver.properties] [mode=<quickCheck | extensiveCheck>] [logLevel=<errors | warnings | infos>]Usually the default parameters are enough to verify the indexes integrity.
application is jts, ccm, qm or rm.
teamserver.properties defaults to conf/jts/teamserver.properties if not specified.
quickCheck is the default verification mode selection. extensiveCheck, is a more expensive operation and verifies every Lucene index. It also reads and verifies all the Jena quads.
logLevel defaults to errors. The warnings log level display information about discrepancies found in the indexes. Warnings do not mean that the indexes are corrupted. If the indexes are corrupted it is clearly reported when the command is completed. Warnings usually mean that there are more indexes that we expect and this could affect performance and results. For example a server not properly shut down could cause this situation and could easily be resolved by restarting the server. The infos log level is mainly useful for debugging purpose.
For example, to verify the JFS indices for the JTS using extensiveCheck verification mode and logging warnings only would be:
repotools-jts.bat -verifyJFSIndexes mode=extensiveCheck logLevel=warningsCheck complete command syntax details here.
Synchronizing indices
As of 5.0.1, a repotools command exists to explicitly force synchronization of the JFS indices with the database. The syntax is as follows:repotools-<application> -synchronizeJFSIndexes [teamserver.properties=conf/<application>/teamserver.properties]
application is jts, ccm, qm or rm.
teamserver.properties defaults to conf/jts/teamserver.properties if not specified.
For example, to synchronize the JFS indices for the JTS would be:
repotools-jts.bat -synchronizeJFSIndexesCheck complete command syntax details here.
Related topics:
External links:
- Backup the Rational solution for Collaborative Lifecycle Management
- Repotools Command Reference for rebuilding JFS indices at InfoCenter
- Repotools Command Reference for rebuilding Fulltext indices at InfoCenter
- Jazz work item 245648: Backing_up work item indices require a server shutdown
Contributions are governed by our Terms of Use. Please read the following disclaimer.
Dashboards and work items are no longer publicly available, so some links may be invalid. We now provide similar information through other means. Learn more here.