This section describes the testing topologies used for performance tests focused on RTCEE features for Application Development for z/OS.
 From the diagram, we can differentiate:
From the diagram, we can differentiate:
 From the diagram, we can differentiate:
From the diagram, we can differentiate:
 From the diagram, we can differentiate:
From the diagram, we can differentiate:
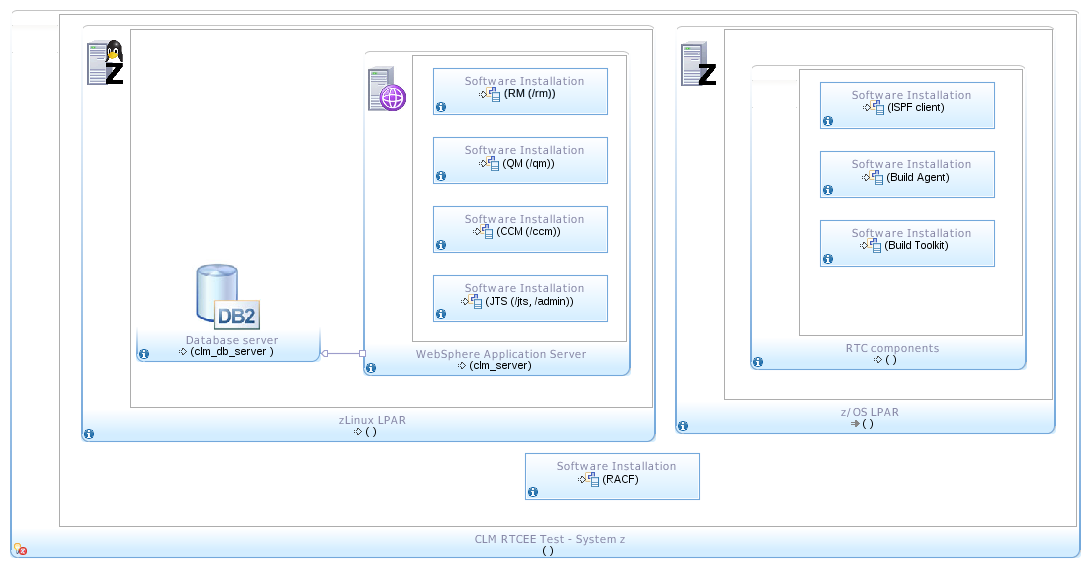
Single Tier Topology: zLinux
 From the diagram, we can differentiate:
From the diagram, we can differentiate:
- Server components are installed in a zLinux LPAR where CLM server and database server are deployed. In spite that the tests are focused on RTC Enterprise Extensions capabilities, the software installation includes the full CLM solution.
- A z/OS LPAR in the same system Z holds the installation of the RTC build components (Build Agent and Build Toolkit), and the RTC ISPF client.
- Both LPARs are dedicated to the CLM components described.
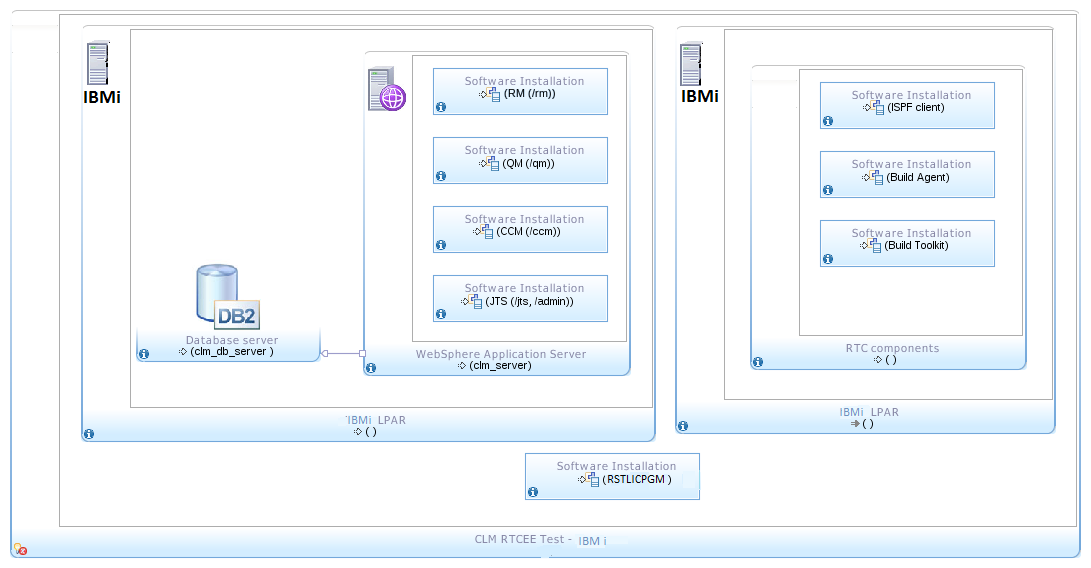
Single Tier Topology: IBMi
 From the diagram, we can differentiate:
From the diagram, we can differentiate:
- Server components are installed in a IBMi LPAR where CLM server are deployed and DB2 server is used. In spite that the tests are focused on RTC Enterprise Extensions capabilities, the software installation includes the full CLM solution.
- A IBMi LPAR in the same IBMi system holds the installation of the RTC build components (Build Agent and Build Toolkit).
- Both LPARs are dedicated to the CLM components described.
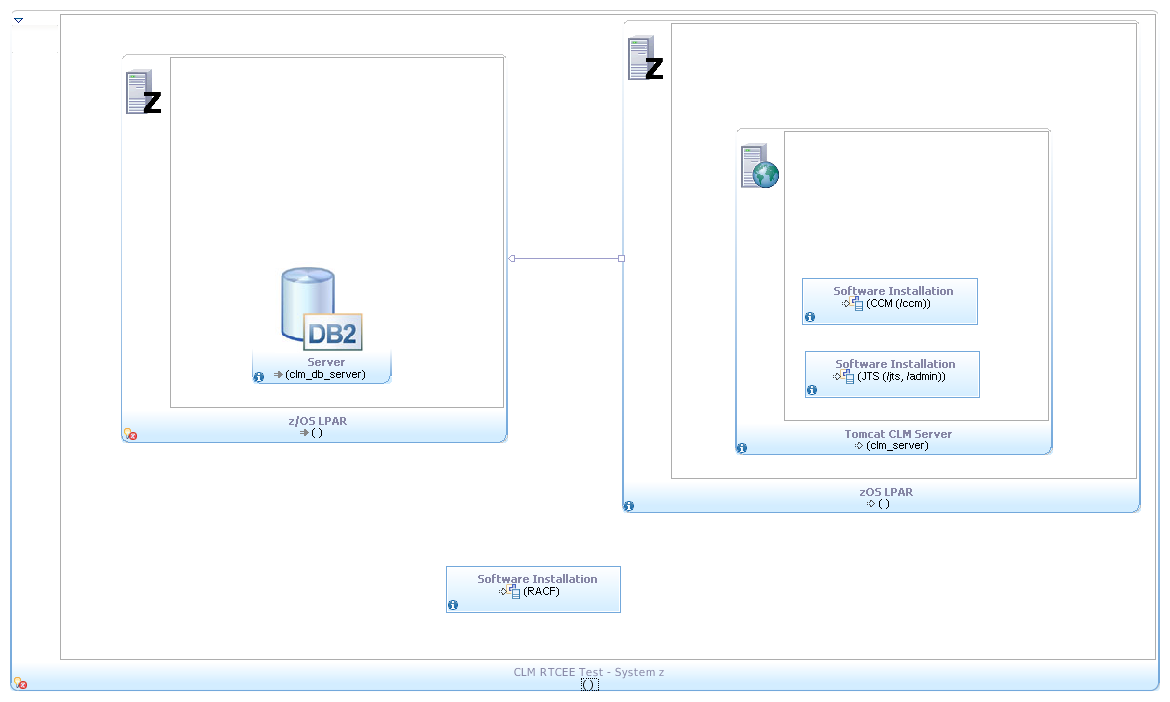
Dual Tier Topology: z/OS
 From the diagram, we can differentiate:
From the diagram, we can differentiate:
- RTC Server components are installed in a z/OS LPAR.
- A z/OS LPAR in the same system Z holds the installation of both the DB2 database and the RTC build components (Build Agent and Build Toolkit).
- Both LPARs are dedicated to the CLM components described during the testing
Contributions are governed by our Terms of Use. Please read the following disclaimer.
Dashboards and work items are no longer publicly available, so some links may be invalid. We now provide similar information through other means. Learn more here.