Ranking in Rational Team Concert 4.0.5
Prioritization is an important role in daily work. The Ranking feature in Rational Team Concert (RTC) helps you to organize and prioritize work items in a plan. Since RTC 4.0, we added a stack-based ranking method, now called “attribute-based ranking”, which is used to rank work items in a plan. Since RTC 4.0.3, we added a new explicit ranking method. Explicit ranking includes a new sorter and rank attribute that makes ranking in a plan clearer and easier to use. In RTC 4.0.5, based on customer preference, we are deprecating attribute-based ranking. We are providing a “Migrate Rank” feature to allow plans that use the attribute-based ranking to migrate to the new explicit ranking.
Note:
- All plans created after adopting RTC 4.0.5 use the new explicit ranking, and the attribute-based ranking method is not available for these plans (see the details in Part 1).
- For those existing plans using the old-attribute based ranking, we provide the Migrate Rank feature that allows migration from the old attribute-based ranking to the new explicit ranking (see the details in Part 2).
Part 1: Explicit ranking in a new plan after adopting RTC 4.0.5
Plans created after adopting RTC 4.0.5 use explicit ranking, by default. The sorting mode “Ranking,” as shown below, refers to the new “explicit ranking” mode and is set, by default, when creating a plan. The following example shows a new unranked plan that will be ranked using the explicit ranking method.
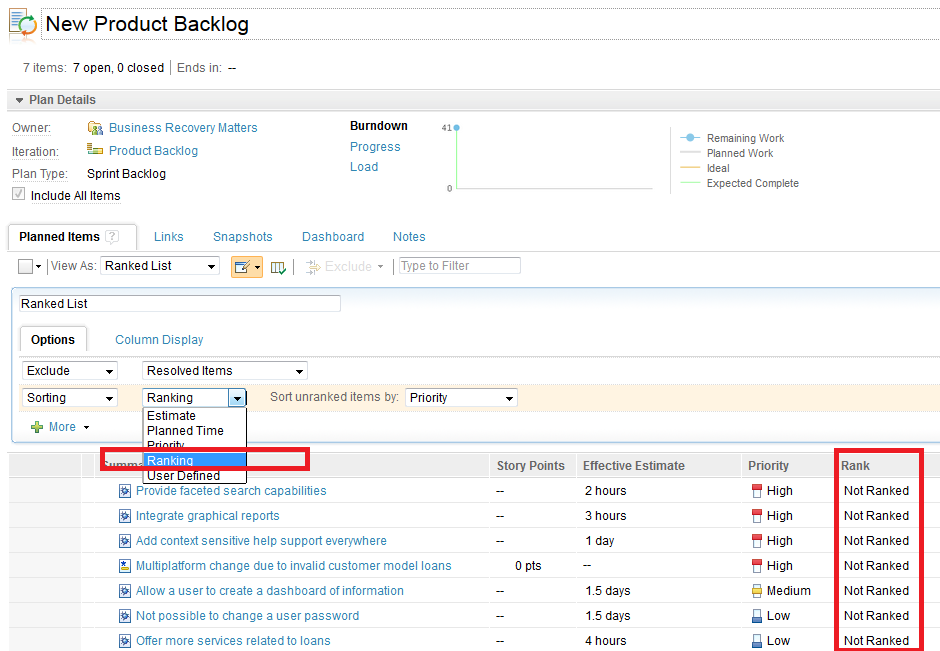
How does the new explicit ranking work?
1) If an item has a rank, its position in the plan is determined by its rank value. Ranked items are listed first, followed by unranked items.2) If an item does not have a rank, its position is determined by the value of the attribute used as a sorter for unranked items. For example, high-priority items come first, followed by all of the medium-priority items and then all of the low-priority items.
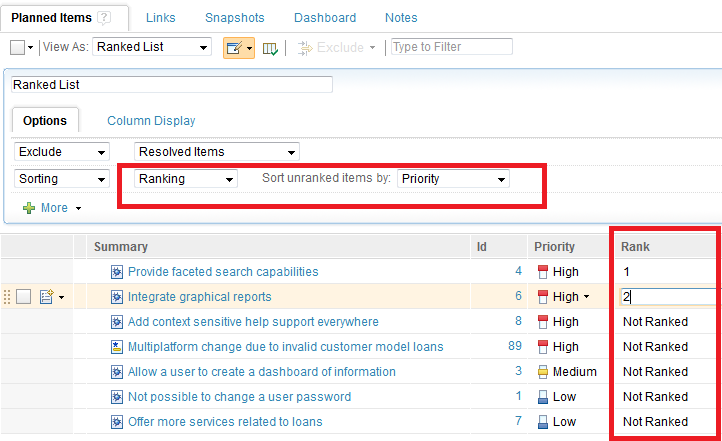
Options to rank within a plan
You can rank items (or remove rank) within a plan using four different methods:
- The Apply Rank action
- Context-menu options
- Drag-and-drop action
- Rank Integer Edit action
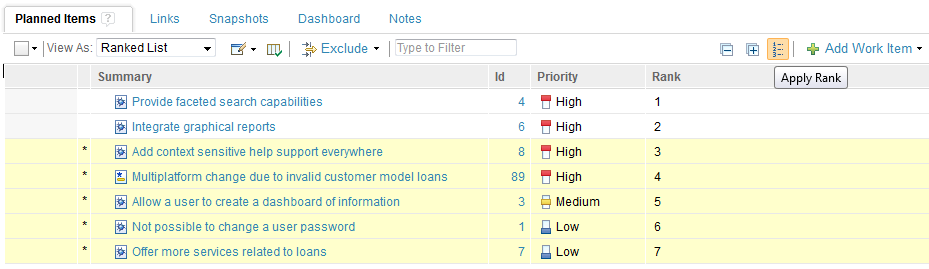
Apply Rank action
The apply rank option is a global action that ranks all items in a plan at the same time. Performing this action assigns a rank value to all items in a plan, in serial order, based on the current position of the items in the plan.
Note:
- If all items are ranked, Apply Rank does nothing, and the plan does not show changes. However, if some of the items are ranked through other options, or if items are hidden from the plan through filtering but were previously ranked, clicking Apply Rank causes the rank to be removed from these items, and the plan changes to an unsaved state.
- If the view has any other sort specified but is configured as a grouped or hierarchical view, the Apply Rank action is disabled as these scenarios are not currently supported.
Context-menu options
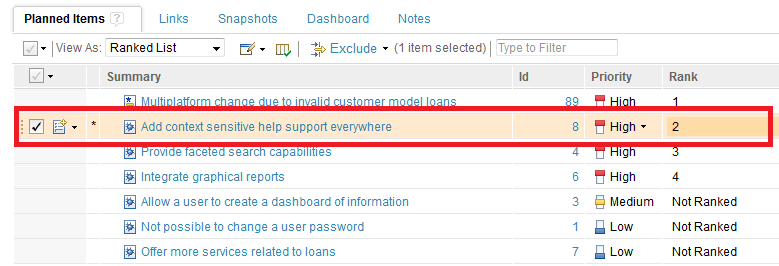
1) Remove Rank: This action removes the rank associated with the item. If the item is not currently ranked, it is disabled. In the following example, the operation is applied to the item, “Add context sensitive help support everywhere.”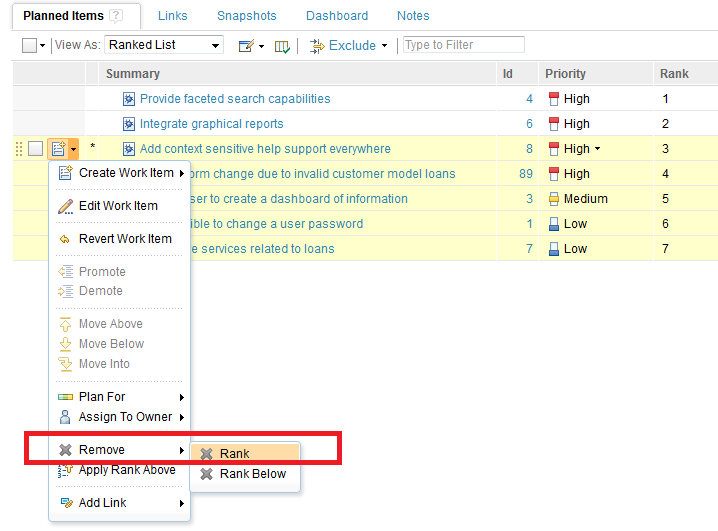

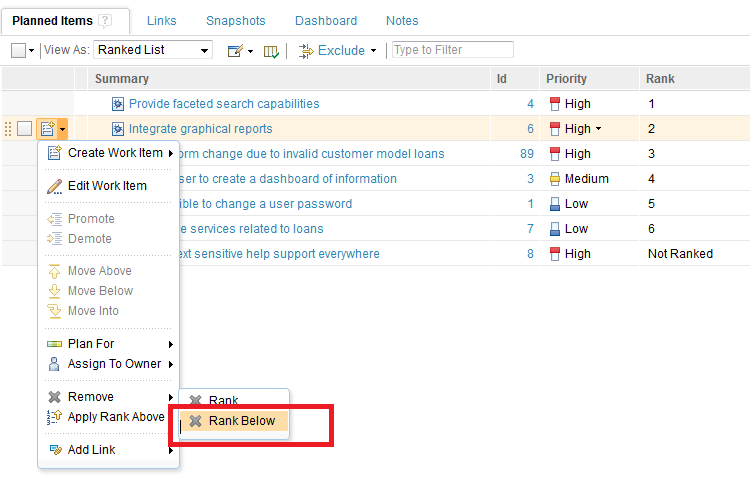
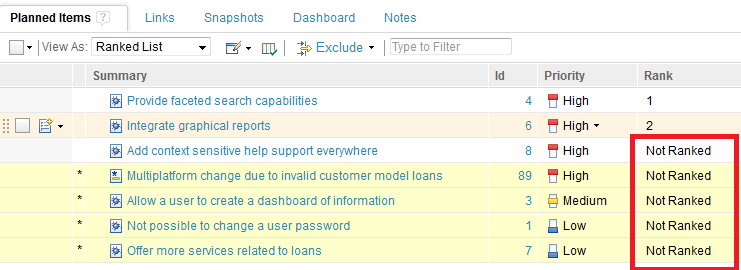

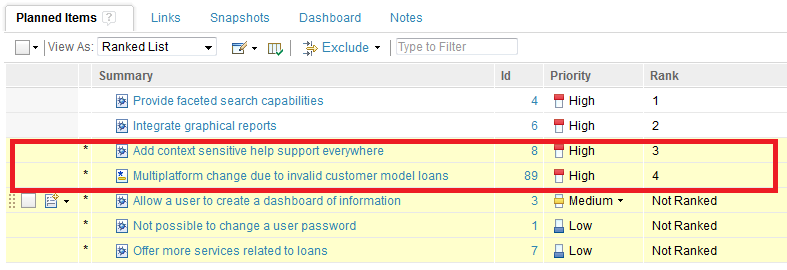
Drag and Drop
Although drag and drop existed in the previous ranking model, there are a few changes in its behavior in the new model.
1) If you drag an item to the top of a plan, it is assigned the rank “1,” and the ranks of all ranked items below it are increased by 1, as shown in the following example when the item, “Multiplatform change due to invalid customer model loans,” is dragged to the top of the list.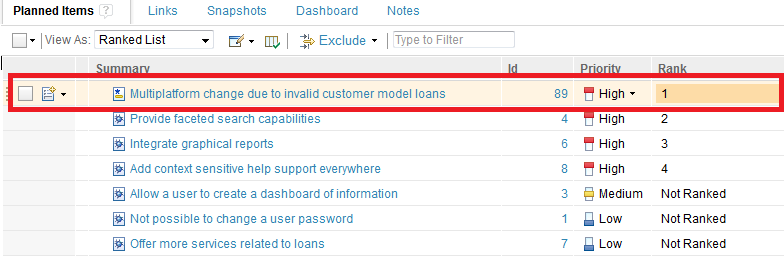
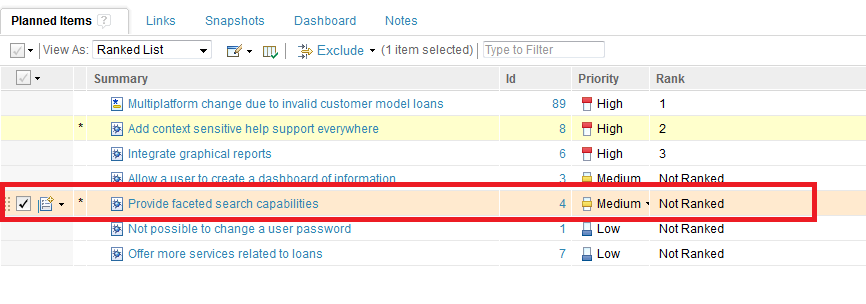
- The scenario mentioned in the third point of the drag-and-drop method is not applicable to a user-defined sorter for unranked items, where although the item loses its rank, its sort attribute for unranked items is not changed to that of its predecessor. When dragging an item into a group of unranked items, it loses its rank, but its sort attribute for unranked items does not change.
- Dragging an item from the bottom of the list to the top applies changes that need to be saved only to the top item and not the other items, even though they get new ranks. This is because ranks are calculated based on a hidden sequence value. Since only the top item’s sequence value changes, it needs to be saved.
Rank Integer Edit
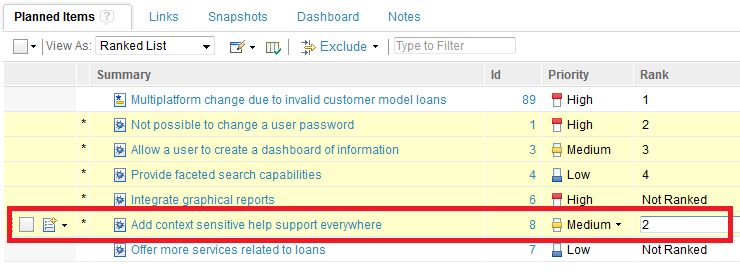
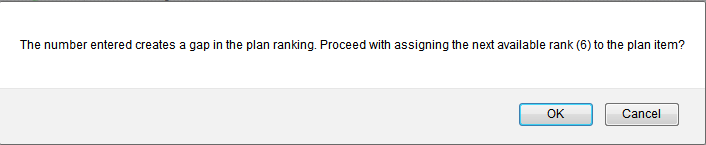
You can also directly edit the rank value of an existing item to specify a integer rank. Click the rank cell that corresponds to the rank that you want to change, and type the rank value.
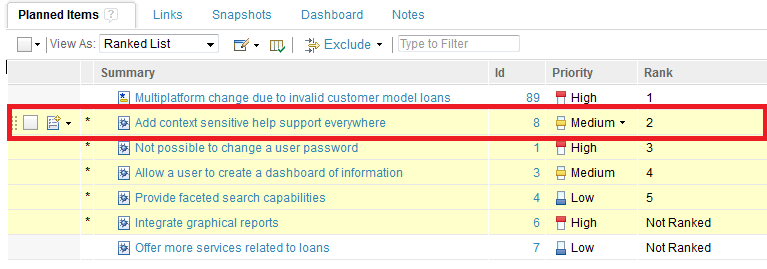
Based on the rank number that you type, the item and all subsequent ranked items are re-ranked accordingly. In the following example, a rank value is given to the item, “Add context sensitive help support everywhere.”
Creating a custom sort attribute for unranked items
The sort attribute for unranked items drop-down list is populated by the existing enumerations in the system. To create a custom sort attribute for unranked items, you must create a custom enumeration. You can find more information on creating a custom enumeration at Using a Custom Ranking Attribute for Planning.
In the following example, the Importance column is a custom attribute with four categories: Not Important, Light, Essential, and Crucial. The weight of the items increase from lowest to highest. In an unranked plan with items having their importance assigned, setting the secondary sort attribute to the Importance enumeration results in a sorted order, as shown in the following example.
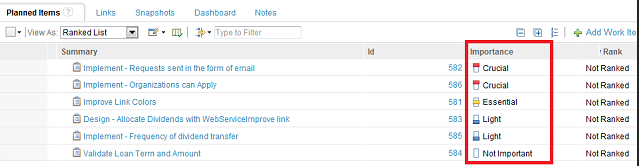
You can see that the plan is now using the Importance attribute for the plan item during sorting. All the unranked plan items (in this case, all of the items) are now sorted according to their importance, starting with the most important to the least important.
Part 2: Migrating to explicit ranking after adopting RTC 4.0.5
The Migrate Rank action allows migration from the old attribute-based ranking to the new explicit ranking. This feature is only applicable for those existing plans that were created before adopting RTC 4.0.5 and that use the old attribute-based ranking.
Enable Migrate Rank action
The Migrate Rank action is enabled when the plan has no unsaved changes and is in a flat-list view with no groups or hierarchical displays. The following example shows an existing plan using the attribute-based ranking.
Note: The Migrate Rank action is disabled when the plan has unsaved changes, and it is not supported for grouped and hierarchical views. You must save the plan and view it in a flat view to enable the Migrate Rank action.

After the Migrate Rank action:
- The discontinuous attribute-based ranking (for example, 1, 2, Not Ranked, 3, 4, 6, 7), becomes consecutive in explicit ranking (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, Not Ranked).
- The unranked items remain “Not Ranked” and are sorted to the bottom of the list.

After the migration, you can switch back to the attribute-based ranking by selecting the attributed-based mode in the Plan Details section of the plan. In this following example, the attribute is “Priority,” which is the default ranking attribute. Changing to Priority switches the mode back to attribute-based ranking. You can switch back and forth between attribute-based and explicit ranking. The changes take effect after saving the plan.

For additional information about the topic presented in the article add your comments or questions directly in the discussion part, or visit our Jazz.net Forum.
Copyright © 2013 IBM Corporation