Enabling Rational Team Concert Work Item Synchronizer to display field properties of the source system
Summary
For migrating data from one system to another, mapping between the data elements of both systems needs to be established. Based on this mapping, data from the source system is populated into the target system. Rational Team Concert (RTC) facilitates this data synchronization between itself and other third party systems through the ‘Synchronization Rule’ editor. This editor displays all the attributes of an RTC work item which can be mapped to corresponding attributes on the other system. Attribute names on the other system can be entered manually for the required work item. This approach works fine in cases where a small number of field mappings are to be done, and for cases where field names are static in the source system. However, it can be a challenging task in cases where field names of the other system are customizable. For example, different project templates for different projects. Handling each of them manually is often frustrating as any typographical error leads to rework.
The RTC work item framework provides a mechanism to fetch the attribute names, and their literals programmatically from the external system. This is then populated in a drop down list in the sync rule editor, which can be used for mapping by list element selection. This article explains how to use these RTC methods and classes to get the external fields list pre-populated in sync rules.
Overview
Rational Team Concert (RTC) is a tool used for collaborative project planning and change management. Project planning pieces are managed by work items and their attributes. Each attribute is a data element which helps in the management of project process.
Similarly other project planning and change management tools also have their set of attributes which help in project process management. The challenge arises when data from this system needs to be imported to RTC or vice versa.
Here synchronization rule plays a vital role when connecting RTC to any other project planning and change management tool. Synchronization rule defines mappings between the attributes and literals for those attributes. Using the synchronization rule one can also write transformations between attribute values of the two systems and create dependency between RTC attributes to reflect those present in the source system.
RTC item connector framework facilitates adding values to sync rule programmatically. It uses the external repository information from external repository connection to connect to the external system. Post connection it fetches attributes and literals of the external system from this connection.
Implementation
Item connector framework provides three components that need to be developed to enable synchronization between RTC and external system. One of these components is External repository manager. It is implemented as a Jazz server extension, and is invoked whenever outgoing synchronization is triggered for a Jazz item which is connected to an external object. The synchronization rules that are defined in a project area determine which Jazz items associated with that project area will be considered for outgoing synchronization. This plug-in extends class AbstractInteropExternalManager implements IInteropExternalManager interface.
IInteropExternalManager interface has an optional method getSupportedTypeInfo, which is overridden to gather information about the external types supported by the external system for connection with Jazz items. The type information includes the names of the object types, as well as the names of the properties they have (which can be mapped to from Jazz properties), and other information about the properties (such as whether they have enumerated values). This information is presented in the synchronization rule editor. It populates choice lists for the various fields that apply to the external object.
Method implementation is as follows:
public ITypeInfoDTO[] getSupportedTypeInfo(final IExternalRepositoryConnection externalConnection){ final String[] typeInfoArray = { "CMVCDefect", "CMVCFeature"}; final List<ITypeInfoDTO> result = new ArrayList<ITypeInfoDTO>(); for (final String o : typeInfoArray) { final ITypeInfoDTO obj = InteropFactory.INSTANCE.createTypeInfoDTO(); if (o.equals("CMVCDefect")) { obj.setName("Defect"); obj.setMappedName(o); } else if (o.equals("CMVCFeature")) { obj.setName("Feature"); obj.setMappedName(o); } obj.getProperties().addAll(getPropertyName(o, externalConnection)); } catch (final InteropException e) { ExceptionHandler.handleException(e); throw new RuntimeException(e); } result.add(obj); } return result.toArray(new ITypeInfoDTO[0]); } The method above creates array of all RTC mapped work item types and then set its name to external repository mapped item. In this case ‘CMVCDefect’ is mapped to ‘Defect’ and ‘CMVCFeature’ is mapped to ‘Feature’. ‘CMVCDefect’ and ‘CMVCFetaure’ are customized work item types in RTC. Then we need to add properties for that work item type i.e its attributes and their allowed values, if any
private List<IPropertyInfoDTO> getPropertyName(final String type, final IExternalRepositoryConnection externalConnection) throws InteropException { final List<IPropertyInfoDTO> result = new ArrayList<IPropertyInfoDTO>(); final List<CMVCFieldDefinition> fields = getAttributes(type); for (final CMVCFieldDefinition f : fields) { final IPropertyInfoDTO obj = InteropFactory.INSTANCE.createPropertyInfoDTO(); obj.setIdentifier(f.isIdentifier()); obj.setModifier(f.isModifier()); obj.setName(f.getName()); final String referenceTypeName = f.getReferencedRecordTypeName(); obj.setTransformer(f.getTransformer()); if (referenceTypeName != null) { obj.setReferenceTypeName(referenceTypeName); } final List<String> allowedValues = f.getAllowedValues(); if (allowedValues != null) { obj.getAllowedValues().addAll(allowedValues); } result.add(obj); } return result; } The above method sets properties for each work item type passed to this method. It fetches a list of attributes from repository using method getAttributes. The method takes work item type as parameter and returns a list of objects of CMVCFieldDefinition. For each item in the returned list a IPropertyInfoDTO object is created and then set its attribute name and all its properties. Property name here include: is identifier, is modifier, has reference sync rule attached, require transformer, has allowed values etc.
public List<CMVCFieldDefinition> getAttributes(final String type) { final List<CMVCFieldDefinition> arrayFields = new ArrayList<CMVCFieldDefinition>(); HashMap<String, String> defectAttributeWithType = new HashMap<String, String>(); HashMap<String, String> featureAttributeWithType = new HashMap<String, String>(); final List<String> customDefect = new ArrayList<String>(); final List<String> customFeature = new ArrayList<String>(); final List<String> allAttributes = new ArrayList<String>(); doCMVCLogin(externalConnection); if (type.contains("CMVCDefect")) { defectAttributeWithType = getAttributesFromCMVC(loginInfo, "DefectConfigInfo");//get attributes for (final String string : defectAttributeWithType.keySet()) { customDefect.add(string); } allAttributes.addAll(customDefect); } else if (type.contains("CMVCFeature")) { featureAttributeWithType = getAttributesFromCMVC(loginInfo, "FeatureConfigInfo");//get attributes for (final String string : featureAttributeWithType.keySet()) { customFeature.add(string); } allAttributes.addAll(customFeature); } for (final String attribute : allAttributes) { final CMVCFieldDefinition field = new CMVCFieldDefinition(); try { field.setName(attribute); if (attribute.equalsIgnoreCase("unique_identifier")) { field.setIsIdentifier(true); } if (attribute.equalsIgnoreCase("modifiedBy")) { field.setIsModifier(true); } if (attribute.equalsIgnoreCase("compName")) { field.setTransformer(CATEGORY_TRANSFORMER_CLASS_NAME); } if (attribute.equalsIgnoreCase("originLogin") || attribute.equalsIgnoreCase("ownerLogin") || attribute.equalsIgnoreCase("remarks")) { field.setReferencedRecordTypeName("User"); } if (attribute.equalsIgnoreCase("remarks")) { field.setTransformer(NOTES_TRANSFORMER_CLASS_NAME); } // this if else is required to get allowed values separately for // system owned field, // config fields and state if (attribute.equalsIgnoreCase("state")) { // handle custom states &DSR later field.setAllowedValues(states); } } catch (final InteropException e) { ExceptionHandler.handleException(e); } arrayFields.add(field); }// end for for all attributes return arrayFields; } The method do CMVC login and fetch list of attributes for passed work item type and then creates a CMVCFieldDefinition object of each attribute and set its property.
public boolean doCMVCLogin() { try { CommandResults cmdRes = passwordAuthenticationObject.login( getFamilyInfo(), sessionDataObject, false, 0,mServerVersion); int rc1 = cmdRes.getReturnCode(); if (rc1 != CommandResults.SUCCESS) throw new Exception("Command to login CMVC was not successfull" + cmdRes.getFailureMessages()); else{ return true; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return false; } package com.ibm.sdwb.connector.cmvc.workitem.util; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class CMVCFieldDefinition { private List<String> allowedValues = new ArrayList<String>(); private String name; private String referenceRecord = null; private String transformer = null; private boolean isIdentifier = false; private boolean isModifier = false; public List<String> getAllowedValues() throws InteropException { return allowedValues; } public String getName() throws InteropException { return name; } public String getReferencedRecordTypeName() throws InteropException { return referenceRecord; } public String getTransformer() throws InteropException { return transformer; } public boolean isIdentifier() throws InteropException { return isIdentifier; } public boolean isModifier() throws InteropException { return isModifier; } public void setAllowedValues(final List<String> values) throws InteropException { allowedValues = values; } public void setIsIdentifier(final boolean value) throws InteropException { isIdentifier = value; } public void setIsModifier(final boolean value) throws InteropException { isModifier = value; } public void setName(final String name) throws InteropException { this.name = name; } public void setReferencedRecordTypeName(final String recordType) throws InteropException { referenceRecord = recordType; } public void setTransformer(final String transformer) throws InteropException { this.transformer = transformer; } } Testing and debugging
External repository manager is deployed on RTC as server side plugin. The method to deploy is available in the links section of this article. After the service is deployed, see the synchronization rule view and create an ‘External Repository Connection’. To this connection then add the new synchronization rule. Select ‘External Repository Connection’ created above and ‘External Repository Manager’ plugin deployed on server and then select ‘External type’, you will soon see a message “Fetching external type information” on the top of synchronization rule.
Fetching external type information

It used the information in external repository connection to login to the external system and fetch its details using the method written in the plugin. The first call goes to getSupportedType info and there on the entire list is fetched. You can see list of attributes corresponding to work item type selected in ‘External type’ combo, when you click on add button on right side of ‘Property Mappings’ view. The ‘Define Property mappings’ window will display external repository attributes in combo ‘Choose an external property to map from:’. The other combo ‘Choose an item property to map to;’ displays jazz repository attributes.
Attribute list populated

In case any attribute has literals, it will be displayed in value mapping window.
Literals displayed

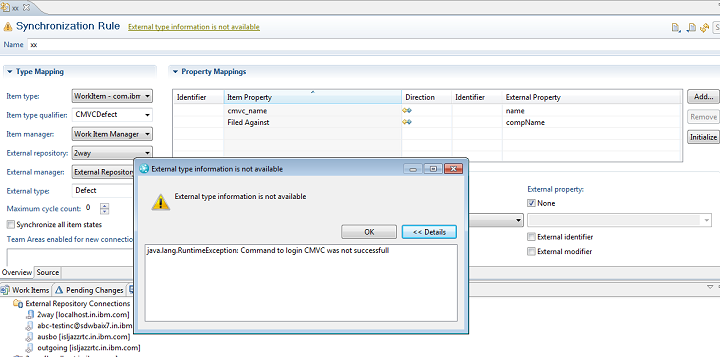
In case of any error in contacting external repository, message displayed in synchronization rule view would be ‘External type information not available”. On clicking this message it open the details, to show the problem. The message displayed depends on code written for handling error conditions.
Error message displayed
The code can be debugged by enabling remote debugging for plugin ‘External Repository Manager’ and putting breakpoint in getSupportedTypeInfo method. The method is called each time sync rule is opened / refreshed / saved. The method is called even if outgoing synchronization is disabled.
For more information
- https://jazz.net/wiki/bin/view/Main/UsingJazzProvisioner
- http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/rational/library/synchronize-cmvc-data-rational-team-concert-data/index.html
- https://jazz.net/wiki/bin/view/Main/ItemConnectorCreation#Introduction
About the authors
Megha Mittal is part of Rational Corp Tools team at IBM Software Labs, in India and working on RTC integrations with IBM legacy systems. Megha holds a master’s degree in computer application and has eight years of experience in application development, primarily in Java technology. She can be contacted at mmittal1@in.ibm.com.
Siddharth Kumar Saraya is working as Technical Lead for Rational at IBM Software Labs. He has completed Dual Masters degree, one in Computer Application and second in Business Administration with majors as Risk and Insurance Management. A summary of the experiences gained over the number of years are manual, automation testing, involved in delivery of projects and managing project teams from project initiation till deployment. He can be contacted at Siddharth.Kumar.Saraya@in.ibm.com
Copyright © 2012 IBM Corporation