Work Item Customization in Rational Team Concert
The Work Item component can be customized in various ways. These customizations are configured on the Process Configuration page of the Project Area or Project Template editor. This article covers both RTC 1.0 and RTC 2.0. The screen captures are from RTC 2.0 but they still apply to RTC 1.0 since the UI hasn’t changed much in RTC 2.0.

Customization Constraints
When customizing work items, some actions should only be done with careful attention, especially when using running project areas. Removing elements like enumeration literals, work item types, workflow states and actions is dangerous as there can be data in the repository referencing such elements. The UI will work with such nonexistent data in most cases by just showing the ID of the element instead of the name. But functionality might be really broken: think of a no longer existent workflow state that provides no actions to transition back into an existing state.
“Safe customizations” are customizations that either add new elements (e.g. work item types) or only change UI related features like display names or editor layouts. The Tech Note “Work Item Customization – Best Practices” explains in more detail how to customize in a safe way.
Before going into the details of the individual work item customizations, here is one issue that affects three customizations:
![]()
Work Item Types and Custom Attributes
You can define your own work item types. Types are organized into type categories that share common behavior like workflow, required properties and the set of attributes.You can define custom attributes for work items to extend the list of built-in attributes. Custom attributes are available for all work item types of a specific type category.

Supported attribute types:
- String
- String attributes, available in three sizes: Small String (250 bytes when using UTF-8 encoding), Medium String (1000 bytes) and String (32768 bytes). String can only be queried by fulltext.
- HTML
- HTML attributes, available in two sizes: Medium HTML (1000 bytes of xml text (including tags) when using UTF-8 encoding) and HTML (32768 bytes of xml text). HTML can only be queried by fulltext.
- Timestamp
- Timestamp
- Integer
- Integer
- Long
- Long
- Boolean
- Boolean
- Enumeration
- Enumeration types are referenced by setting the custom attribute type to the ID of the enumeration. The enumeration has to exist before it can be used as a custom attribute. Conceptually, every enumeration introduces a new attribute type.
- Category
- Work Item Category
- Contributor
- Contributor
- Contributor list
- List of Contributors
- Deliverable
- Deliverable
- Iteration
- Iteration
- Process Area
- Project or Team area
- Process Area list
- List of Project or Team areas
- Project Area
- Project Area
- Project Area list
- List of Project areas
- Tag
- Tags
- Team Area
- Team Area
- Team Area list
- List of Team areas
- Work Item
- Work Item
- Work Item list
- List of Work Items
To force an attribute to be set on work item save, an attribute can be specified to be required (Configuring Project and Team Areas for Work Items).
Defining Enumerations
Enumerations are used as a type for custom attributes. You can define the set of literals and their order. One literal has to be declared as the default value. Since RTC 2.0 one literal can be declared as the Unassigned value which makes it possible to configure the enumeration as a required attribute. Priority and Severity – as used in the Defect work item type – are examples for enumerations.
Workflows – State Transition Policies
For every work item type category you can define a state transition policy – or short: a workflow – that applies to all work item types within that category. A workflow defines the states that a work item can be in and the actions that users take to move the work item from one state to another. Typically, a workflow starts with an New or Submitted state and ends with a state that reflects the final disposition of the work item, such as Finished.You may also specify resolutions, which are optional and refine the meaning of a certain state.
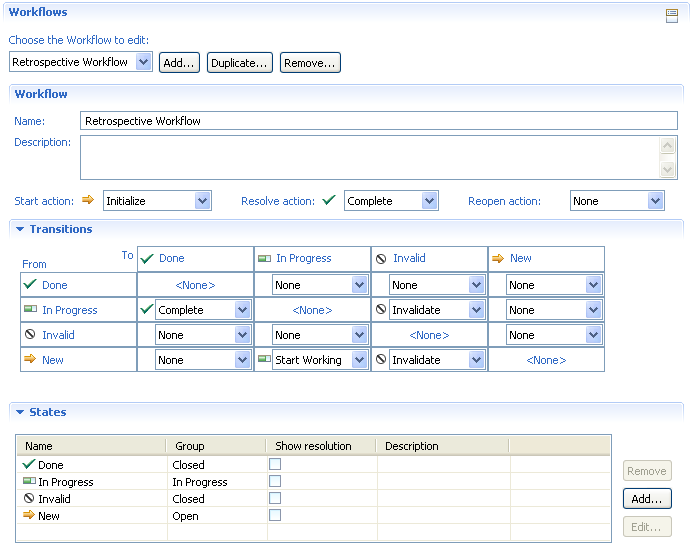
You can create a new workflow either by starting from scratch or by duplicating an existing workflow. In the former case start a new workflow by creating the states of your workflow first.
For every state try to select a so called group that associates a predefined semantic with the state. For example, the open group would be appropriate for the New state.
After your are done with the states, the Transitions section shows a matrix where the row headings contain the from state, and the column headings contain the target state. The intersecting cells contain the actions that users take to move the work item from the from state to the target state. To add an action, select New Action from the drop down menu or select an existing action. At a minimum, provide actions to enable users to move the work item from its original state to its final state.
Newly created Work Items are placed into their initial state by the action selected in the ‘Start action’ menu.
Optionally, if your workflow supports the semantics of ‘Reopen’ or ‘Resolve’, you can select the corresponding actions from the ‘Resolve action’ or ‘Reopen action’ menus.
After you are done with your workflow you have to bind it to a work item type category: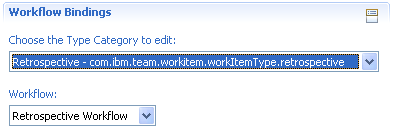
Approval Trackings
You can define approval trackings to trigger workflow actions when an approval changes to a certain state. For each workflow, the approval types Approval, Review and Verification can be configured to trigger an action when entering the Approved, Rejected or Pending state.![]()
Editor Presentations and Quick Information
This sections gives a short overview over the configuration of Editor Presentations and Quick Information. More in-depth information about the configuration is available in the Work Item Editor Presentations article. Developer information about extensibility of editor presentations is available on the wiki as ContributingAttributePresentations.
You can specify the structure of the Work Item Editor in terms of tabs, sections and presentations (a presentation is the UI of a real or synthetic attribute of a Work Item). This structural information is used for both the Eclipse UI and the Web UI but with slightly different layouts. A tab has a certain layout which defines slots. The sections are configured to show up in such a slot, showing their presentations in the specified order. Since RTC 2.0 the editor header can also be configured like an individual section.
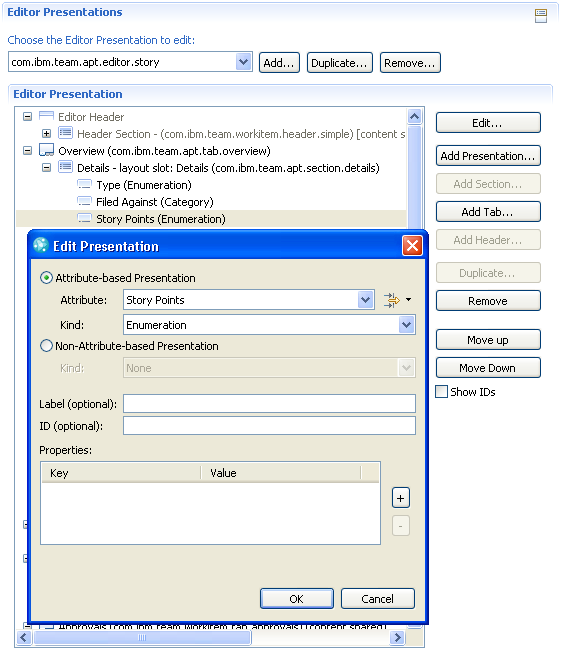
The Quick Information section (shown on the Overview tab in the default editor) is itself configurable by means of another configuration editor. It allows to specify the content of the section and the order of the entries.
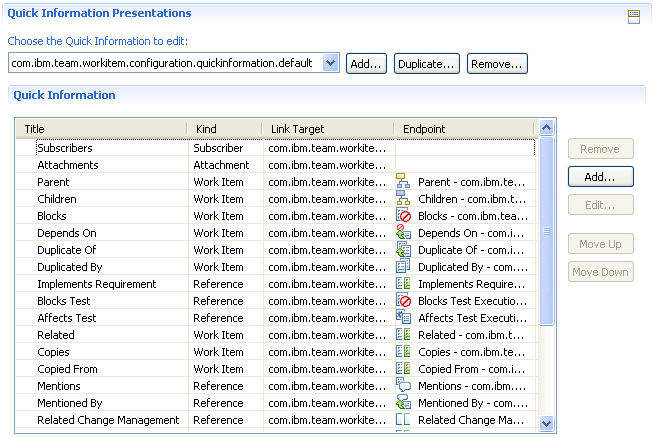
The quick information configuration has to be set as a property of the Quick Information presentation in Editor Presentations. The property is named quickinformationConfiguration, the value is the ID of the configuration.
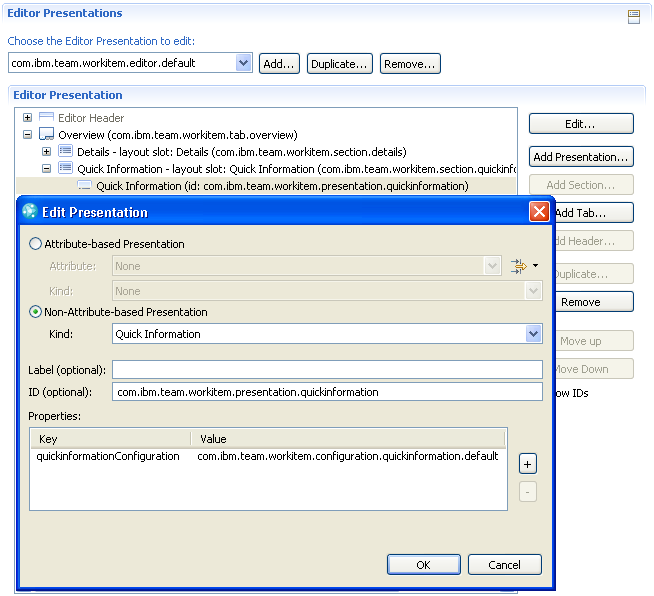
The Work Item component provides presentations for the most common attribute types, but it is possible to contribute custom presentations, be it to display an attribute in a specific manner or to include arbitrary information in the editor.
Each work item type can be bound to an editor. Types without an assigned editor will use the default editor (which can also be modified). Since RTC 2.0 the presentations configuration is not only used for the Work Item editor but for additional UIs, like Plan Preview Pane and Web Inline editor. For these places, individual bindings are configured.

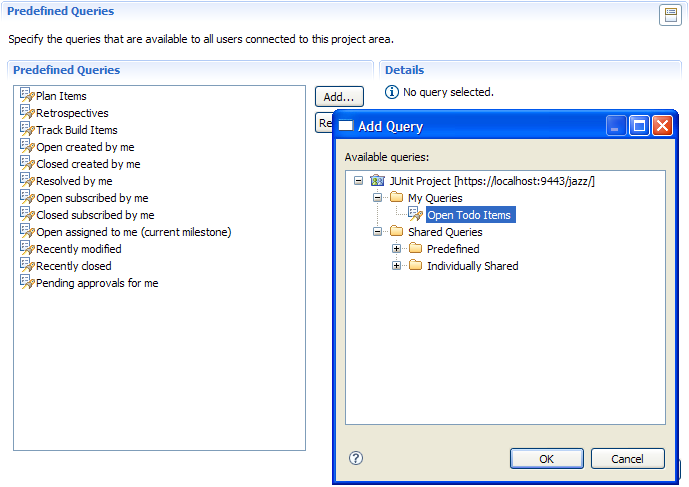
Predefined Work Item Queries
You can configure predefined queries, which will be available to all users in the project (See Sharing Queries if you want to share queries with a team or individual users):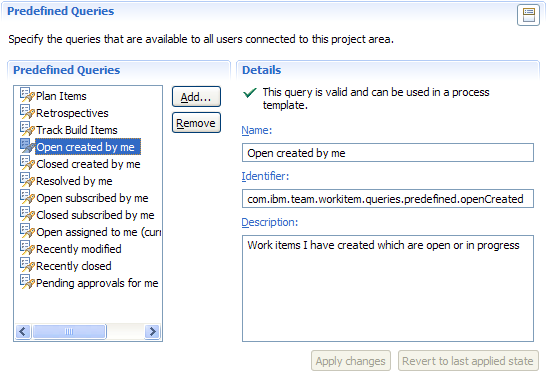
Change Management Type Binding
Since RTC 2.0 the OSLC (http://open-services.net) change management record types can be bound to specific Work Item types. With this it is possible that other applications that communicate with RTC based on the OSLC specification can rely on the existence of specific record types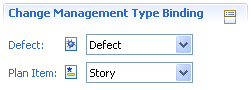
Example: Todo items
In the following example we will introduce a new work item type “Todo” with a custom attribute of type enumeration. The type has its own workflow, its own editor layout and a predefined query.Work item type
Let’s first create a new work item type with a new work item category (the category is used to bind the workflow to the work item type).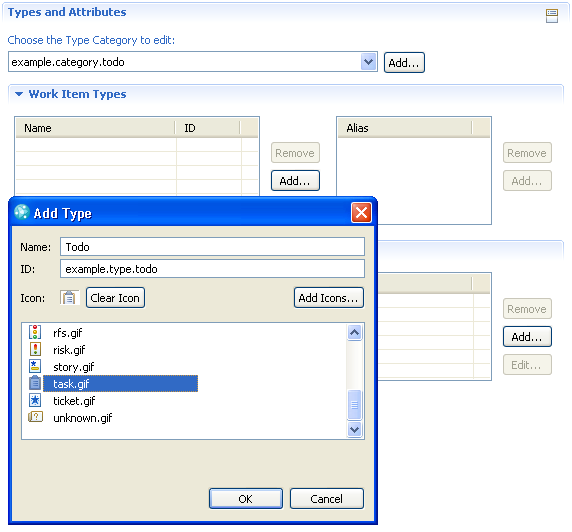
We also want to have a custom attribute named Importance which is an enumeration. Before declaring that custom attribute, we need to create this enumeration.
Enumeration
The importance enumeration has three possible values: Low, Medium and High, where Medium is the default.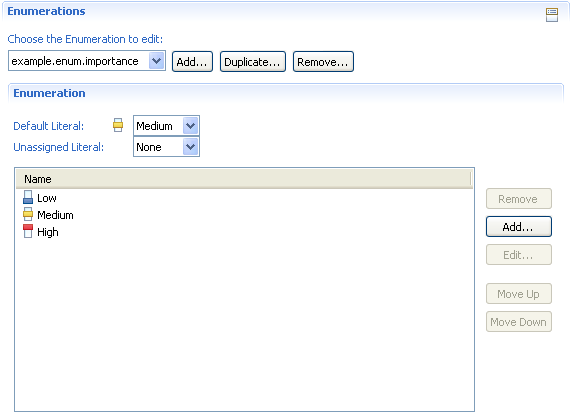
Custom Attribute
Now that the enumeration is defined, we go back to the Types & Attributes editor and add a custom attribute to our type category. As type we useexample.enumeration.importance 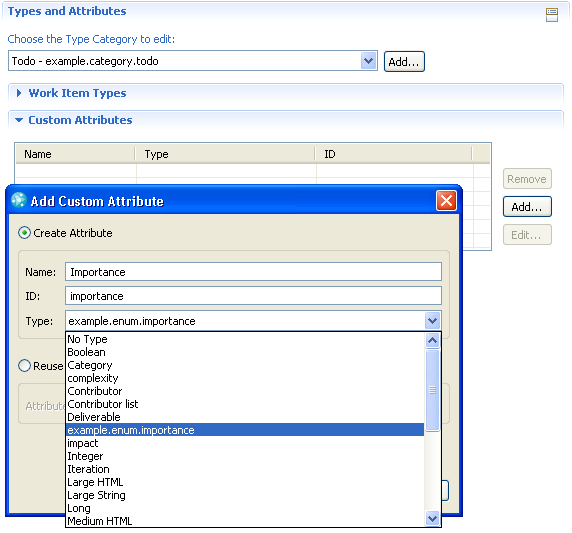
Required Property
Our Todo work item should always have a due date set. We enforce this by marking the dueDate attribute as required.
Under Team Configuration -> Operation Behavior we select the Everyone cell in the Save Work Item (server) row and edit the Required Properties.

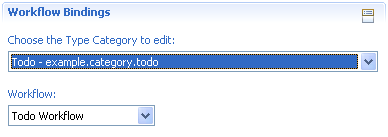
Workflow and Binding
Todo items have a rather short workflow. On creation they enter state open, then they can be closed and once in the closed state, they can be reopened.
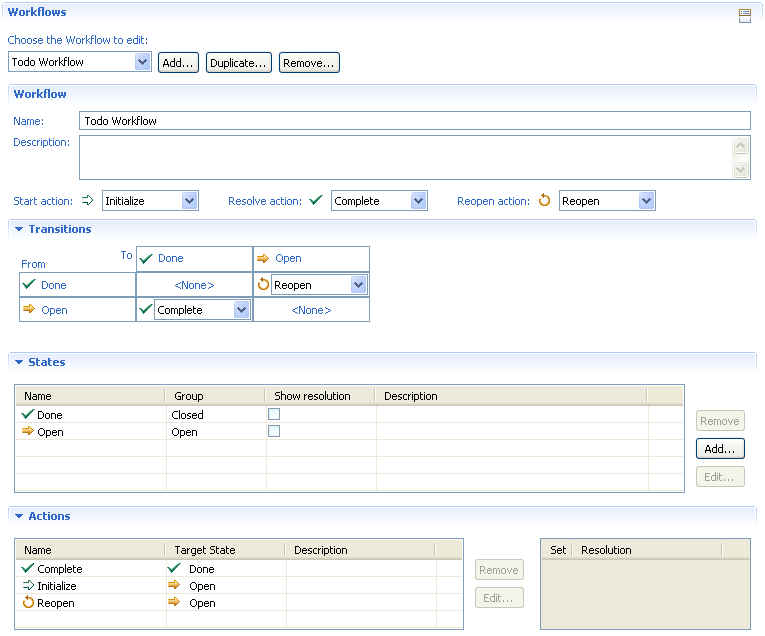
Approval Tracking
We may want to use approvals of type verification after a todo item is closed to signalize that the work is actually done. If the verification is rejected, the todo item should automatically be reopened.![]()
Editor Presentation and Binding
The editor is quite simple. We use only one tab, named Overview with a small details section and a description field. We reuse the description section that is also used by the default editor. Our custom attribute is shown at the top of the details section. As Header in RTC 2.0 we reuse the existing simple header without the resolution field.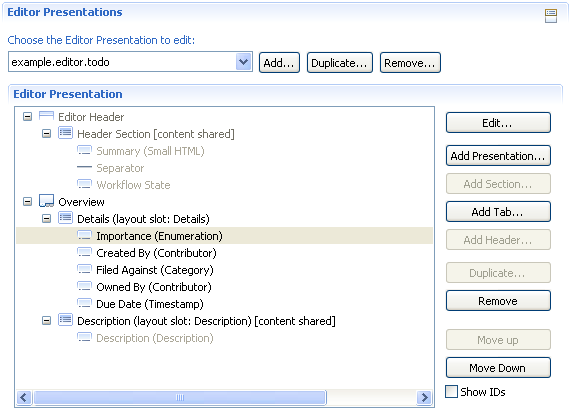
In RTC 2.0 the Created By attribute should not be visible on creation of the item, we thus add the hideIfCreation property.

We bind our type to the created editor. In RTC 2.0 we also bind Plan Preview Pane and Web Inline Editor to our only tab.

Predefined Query
It is important that open todo items can be found quickly. Before a query can be used as predefined query, it has to be created with the query editor.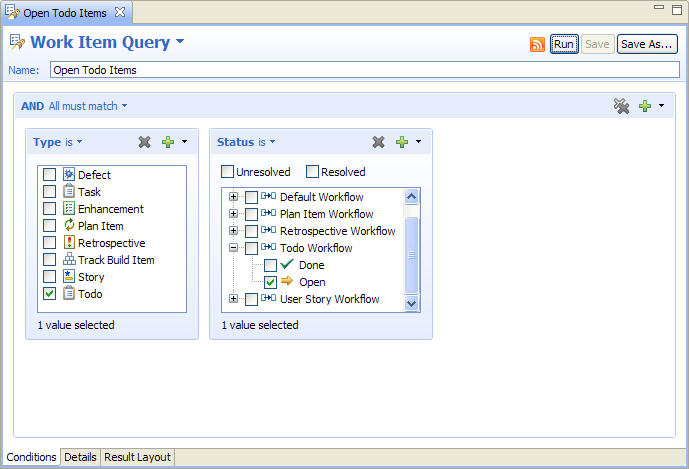
The End
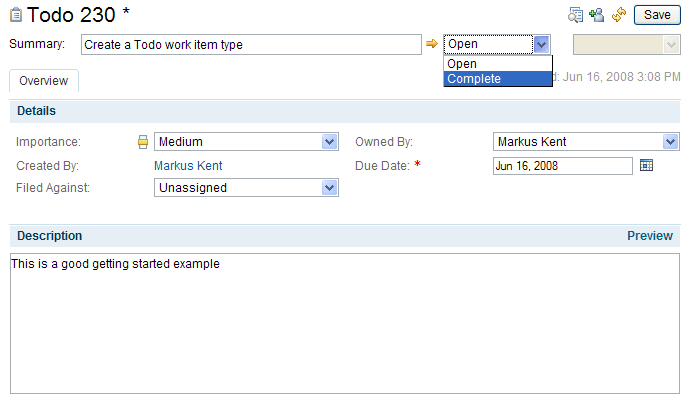
And finally we can create a new work item of type Todo. 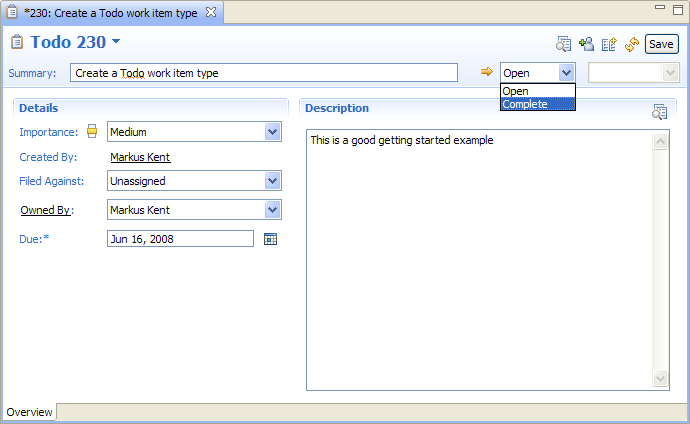
Or use the predefined query to get a todo-list.
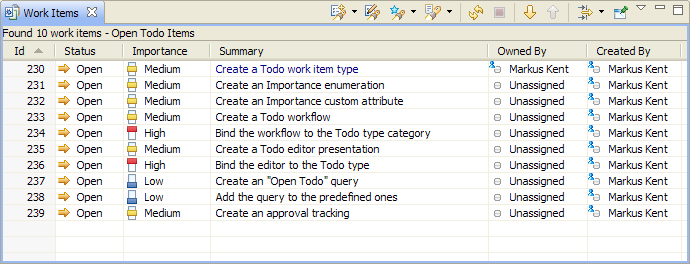
The Todo work item can also be used from the Web UI