Adopting Shift Left
Adoption of Shift Left proceeds similar to any other DevOps adoption effort. See the DevOps Adoption Framework for general
DevOps adoption guidance.
The following table describes how to precede integration testing before unit testing at different
levels of project development:
|
Project Leadership
|
-
Lay out plans that prioritize integration tests as the primary steering
mechanisms
-
Elaborate usage scenarios for 1) highest value and 2) the most uncertainty
-
Tradeoff most important system requirements and attributes such as
changeability, performance, integrity, security, usability, and reliability
|
|
Design/Development
|
-
Develop units, services, and components that are always executable and testable
-
Initial versions permit execution sufficient to satisfy their system interfaces
-
Progress toward more completeness across their entire operational spectrum
|
|
Testing
|
-
Build testing infrastructure, data sets, sequences, harnesses, drivers, and
test cases that permit automated regression testing
-
Define system behavioral tests, usage tests and performance tests first.
-
Then build system coverage tests
|
Applying Shift Left
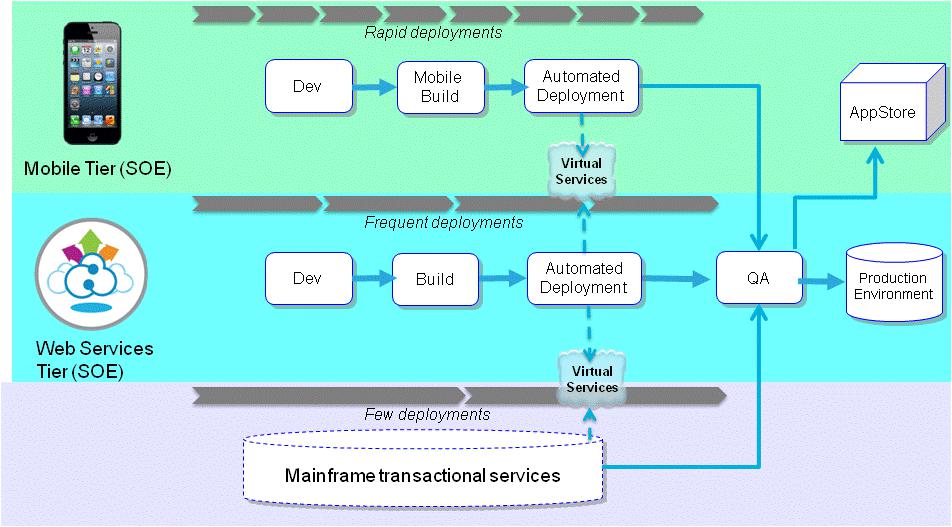
The diagram below shows how a cross functional mobile development project can leverage shift left to
mitigate dependencies, reduce or eliminate integration testing and coordinate activities. The process
for each component of the project is iterative.
The considerations for Shift Left are all undertaken in order to begin test and perform it more
effectively at an earlier point in the software delivery life cycle. It is widely accepted that testing
and defect resolution are more expensive if undertaken at the latter stages of integration as shown in
the graph below.
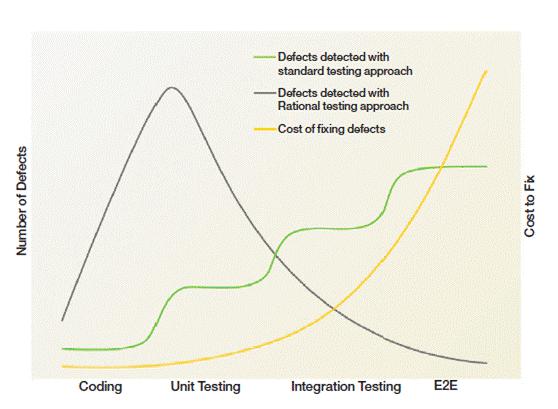
However, the combination of automation and virtualization provide an enabler to actually performing the
testing early without slowing down the delivery pipeline. This graph shows that once Shift Left is
implemented, the impact on costs associated with defects, regardless if the numbers of defects is
constant, will reduce if they are found earlier in the lifecycle.
Practices and Capacity
Continuous Integration, Automated Deployment, and Virtualized Services are key Shift Left practices. They enable
a team to continuously perform integration testing during development.
The capacity of Shift Left or the periodicity you provide feedback to developers is driven by your
objectives for improvement and only constrained by your ability to support the capacity requirements
for each of these practices to support Shift Left. Some excellent papers that dive into these concepts
and practices include:
|
Customer Stories
... More
|